import subprocess
from datetime import datetime, timedelta, timezone
import requests
from datetime import datetime
from apscheduler.schedulers.blocking import BlockingScheduler
scheduler = BlockingScheduler()
# 发送通知请求
def send_msg_to_gotify(title, msg):
url = "http://152.136.153.72:8385/message"
params = {"token": "AI.53prwavAZsoC"}
current_time = datetime.now()
# 表单数据
data = {
"title": title,
"message": msg,
"priority": "0"
}
try:
response = requests.post(
url,
params=params,
data=data
)
print("Response Body:", response.text)
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:
print("请求失败:", e)
def check_ssl_certificate_expiration(web_site, out_date):
# 执行 openssl 命令获取证书信息
try:
result = subprocess.run(
["openssl", "x509", "-in", "fullchain.pem", "-noout", "-dates"],
capture_output=True,
text=True,
check=True,
cwd=f"C:\\Certbot\\live\\{web_site}"
)
except subprocess.CalledProcessError as e:
print("执行 openssl 命令失败:", e)
return
# 解析输出,提取 notAfter 日期
output = result.stdout
not_after_str = None
for line in output.splitlines():
if line.startswith("notAfter="):
not_after_str = line.split("=", 1)[1].strip()
break
if not not_after_str:
print("未找到 notAfter 信息")
return
# 解析日期字符串为 datetime 对象(使用 GMT 时间)
try:
date_format = "%b %d %H:%M:%S %Y GMT"
not_after_date = datetime.strptime(not_after_str, date_format).replace(tzinfo=timezone.utc)
except ValueError as e:
print("日期解析失败:", e)
return
# 获取当前 UTC 时间
current_date = datetime.now(timezone.utc)
# 计算时间差
delta = not_after_date - current_date
# 判断是否在 15 天内且未过期
if 0 <= delta.days <= out_date:
print(f"⚠️ SSL 证书({web_site})将在 {delta.days} 天后过期,请及时续期!")
send_msg_to_gotify('SSL即将过期', f'SSL 证书({web_site})将在 {delta.days} 天后过期,请及时更新并重启nginx服务')
elif delta.days < 0:
print(f"❌ SSL 证书({web_site})已过期!")
send_msg_to_gotify('SSL即将过期', f'SSL 证书({web_site})已过期,请及时更新并重启nginx服务')
else:
print(f"✅ SSL 证书({web_site})有效期超过 {out_date} 天,无需处理。")
# 执行检查
@scheduler.scheduled_job('cron', hour=8, minute=30, misfire_grace_time=3600)
def tick():
check_ssl_certificate_expiration('cx.sdasinfo.org.cn', 15)
try:
scheduler.start()
print('定时任务成功执行')
except Exception as e:
scheduler.shutdown()
print('定时任务执行失败')
finally:
exit()简单的网站都是一套的逻辑爬虫,大家可以参考一下。有兴趣的话帮忙点个start支持一下
前后端系统以及数据库
https://gitee.com/wonder19991209/mohurd\_search\_sys
爬虫脚本
]]>2.检索当日的公告信息,查看是否有科技创新企业,如果有则提醒通知(提醒未写,简单完善数据)
取的关键词模糊搜索+排除词排除掉无关条目,来查找响应数据
检索是否有科技创新企业的公告/通知
# 检查当日数据是否有科创企业名录
import re
import time
import pymysql
import requests
from gxt_spider import get_industry
from kjt_spider import get_sci_kjt
from sdszf_spider import get_sci_sdszf
from jinja2 import Template
import json
def connect_to_database():
connection = pymysql.connect(
host='127.0.0.1',
user='root',
password='123456',
database='my_database_test',
charset='utf8mb4',
cursorclass=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor
)
return connection
def query_today_kc_enterprises():
keywords = [
"科技型中小企业",
"高新技术企业",
"众创空间",
"科技领军企业",
"技术先进型服务企业",
"技术创新示范企业",
"专精特新",
"科技企业",
"瞪羚",
"独角兽",
"科技小巨人企业",
'小巨人']
not_contain_keywords = ["取消","组织申报","认定和复核","申报","补助名单","绩效评价"]
sql = build_sql_query(keywords, not_contain_keywords)
connection = connect_to_database()
try:
with connection.cursor() as cursor:
cursor.execute(sql)
results = cursor.fetchall()
return {
"total": len(results),
"list": results
}
finally:
connection.close()
def build_sql_query(keywords, not_contain_keywords):
like_conditions = " OR ".join([f"title LIKE '%{keyword}%'" for keyword in keywords])
not_like_conditions = " and ".join([f"title NOT LIKE '%{not_contain_keyword}%'" for not_contain_keyword in not_contain_keywords])
sql = f"""
SELECT
CASE type
WHEN '1' THEN '山东省科学技术厅'
WHEN '2' THEN '山东省工业和技术化厅'
WHEN '3' THEN '山东省人民政府'
ELSE '未知类型'
END AS type_name,date,title,url FROM `sci_spider`
WHERE ({like_conditions})
AND ({not_like_conditions})
AND DATE(create_date) = DATE(NOW())
"""
return sql
def mail_sender(content):
import smtplib
from email.mime.text import MIMEText
from email.header import Header
# 第三方 SMTP 服务
mail_host = "smtp.163.com" # 设置服务器
mail_user = "18631839859@163.com" # 用户名
mail_pass = "GENGs7dM45TJDH6y" # 口令
sender = '18631839859@163.com'
receivers = ['wonder1999@126.com'] # 接收邮件,可设置为你的QQ邮箱或者其他邮箱
# message = MIMEText(content, 'plain', 'utf-8')
message = MIMEText(content, 'html', 'utf-8')
message['From'] = Header("科技型中小企业通知", 'utf-8')
message['To'] = Header("科技型中小企业", 'utf-8')
subject = '科技型中小企业通知'
message['Subject'] = Header(subject, 'utf-8')
try:
smtpObj = smtplib.SMTP()
smtpObj.connect(mail_host, 25) # 25 为 SMTP 端口号
smtpObj.login(mail_user, mail_pass)
smtpObj.sendmail(sender, receivers, message.as_string())
print("邮件发送成功")
except smtplib.SMTPException:
print("Error: 无法发送邮件")
def wx_web_hook(data):
"""
通过企业微信Webhook发送Markdown格式的消息
:param data: 包含通知数据的字典,结构应包含'total'和'list'键
:return: None
"""
# Webhook地址(请替换为你的实际Key)
webhook_url = "https://qyapi.weixin.qq.com/cgi-bin/webhook/send?key=ef84945d-2247-4f09-ac0b-be7a6607c24e"
# 构造Markdown内容
content = f"**找到 {data['total']} 条疑似符合条件的记录:**\n"
for row in data['list']:
content += (
f"- [{row['title']}]({row['url']}) "
f"<font color=\"comment\">{row['date']}</font> "
f"<font color=\"warning\">{row['type_name']}</font>\n"
)
# 构建请求体
payload = {
"msgtype": "markdown",
"markdown": {
"content": content
}
}
# 发送请求并处理响应
try:
response = requests.post(webhook_url, json=payload)
response.raise_for_status() # 抛出HTTP错误
result = response.json()
if result.get("errcode") == 0:
print("✅ 消息发送成功")
else:
print(f"❌ 消息发送失败: {result.get('errmsg')}")
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:
print(f"⚠️ 请求异常: {e}")
if __name__ == '__main__':
get_industry(1, 2)
get_sci_kjt(1, 1)
get_sci_sdszf(1, 3)
data = query_today_kc_enterprises()
title = f"找到 {data['total']} 条疑似符合条件的记录:"
for row in data['list']:
print(row)
if data['total'] > 0:
wx_web_hook(data)
# mail_sender('测试消息')工信厅爬虫
import re
import time
import pymysql
import requests
# 数据库链接
def connect_to_database():
connection = pymysql.connect(
host='127.0.0.1',
user='root',
password='123456',
database='my_database_test',
charset='utf8mb4',
cursorclass=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor
)
return connection
def find_new_date():
connection = connect_to_database()
try:
with connection.cursor() as cursor:
sql = "SELECT date FROM `sci_spider` WHERE type = '2' ORDER BY DATE(date) DESC LIMIT 0,1"
cursor.execute(sql)
results = cursor.fetchall()
return results[0]['date']
except Exception as e:
return ''
connection.close()
finally:
connection.close()
def get_industry(page_num, type):
url = (f'http://gxt.shandong.gov.cn/col/col15201/index.html?uid=586830&pageNum={page_num}')
user_Agent = "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/105.0.0.0 Safari/537.36"
headers = {
"Referer": None,
"User-Agent": user_Agent
}
while True:
try:
response = requests.get(url=url, headers=headers)
response.encoding = 'utf-8'
response = response.text
break
except:
print("请求失败,尝试睡眠一会(半小时)")
sleep_time = 60 * 30
time.sleep(sleep_time)
print("睡眠结束,继续运行...")
continue
da = re.findall(r'<div class="bottom"> <span> (.*?) </span>', response)
in_url = re.findall(r'target="_blank" href="(.*?)">', response)
content = re.findall(r'<a title="(.*?)" target="_blank"', response)
for i in range(0, len(da)):
print(str(i+1) + ' : ' + da[i][0:10] + ' : '+content[i]+ ' : ' + in_url[i])
if len(da)*2 != len(in_url) or len(da)*2 != len(content):
print("数据不完整,跳过插入")
return
new_date = find_new_date()
if not new_date or new_date == '':
new_date = '1970-01-01' # 默认最小日期
connection = connect_to_database()
try:
with connection.cursor() as cursor:
sql = """
INSERT INTO `my_database_test`.`sci_spider`
(`title`, `url`, `date`, `type`, `create_date`)
VALUES (%s, %s, %s, %s, NOW())
"""
count = 0
for i in range(len(da)):
if da[i][0:10] > new_date:
count = count + 1
cursor.execute(sql, (content[i], in_url[i], da[i][0:10], type))
connection.commit()
print(f"已成功插入 {count} 条数据")
except Exception as e:
print(f"插入数据失败: {e}")
connection.rollback()
finally:
connection.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
get_industry(1, 2)科技厅爬虫
import re
import time
import pymysql
import requests
def connect_to_database():
connection = pymysql.connect(
host='127.0.0.1',
user='root',
password='123456',
database='my_database_test',
charset='utf8mb4',
cursorclass=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor
)
return connection
def find_new_date():
connection = connect_to_database()
try:
with connection.cursor() as cursor:
sql = "SELECT date FROM `sci_spider` WHERE type = '1' ORDER BY DATE(date) DESC LIMIT 0,1"
cursor.execute(sql)
results = cursor.fetchall()
return results[0]['date']
except Exception as e:
return ''
connection.close()
finally:
connection.close()
def get_sci_kjt(page_num, type):
url = (f'http://kjt.shandong.gov.cn/col/col13360/index.html?uid=85651&pageNum={page_num}')
user_Agent = "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/105.0.0.0 Safari/537.36"
headers = {
"Referer": None,
"User-Agent": user_Agent
}
while True:
try:
response = requests.get(url=url, headers=headers)
response.encoding = 'utf-8'
response = response.text
break
except:
print("请求失败,尝试睡眠一会(半小时)")
sleep_time = 60 * 30
time.sleep(sleep_time)
print("睡眠结束,继续运行...")
continue
da = re.findall(r'<span class="pull-right">(.*?)</span>', response)
sci_url = re.findall(r'href="(.*?)" class="ellipsis-line-clamp">', response)
content = re.findall(r'<s></s>(.*?)</a></li>', response)
for i in range(0, len(da)):
print(str(i+1) + ' : ' + da[i][0:10] + ' : '+content[i]+ ' : ' + sci_url[i])
if len(da) != len(sci_url) or len(da) != len(content):
print("数据不完整,跳过插入")
return
new_date = find_new_date()
if not new_date or new_date == '':
new_date = '1970-01-01' # 默认最小日期
connection = connect_to_database()
try:
with connection.cursor() as cursor:
sql = """
INSERT INTO `my_database_test`.`sci_spider`
(`title`, `url`, `date`, `type`, `create_date`)
VALUES (%s, %s, %s, %s, NOW())
"""
count = 0
for i in range(len(da)):
if da[i] > new_date:
count = count + 1
cursor.execute(sql, (content[i], sci_url[i], da[i], type))
connection.commit()
print(f"已成功插入 {count} 条数据")
except Exception as e:
print(f"插入数据失败: {e}")
connection.rollback()
finally:
connection.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
get_sci_kjt(1, 1)山东省人民政府爬虫
import re
import time
import pymysql
import requests
def connect_to_database():
connection = pymysql.connect(
host='127.0.0.1',
user='root',
password='123456',
database='my_database_test',
charset='utf8mb4',
cursorclass=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor
)
return connection
def find_new_date():
connection = connect_to_database()
try:
with connection.cursor() as cursor:
sql = "SELECT date FROM `sci_spider` WHERE type = '3' ORDER BY DATE(date) DESC LIMIT 0,1"
cursor.execute(sql)
results = cursor.fetchall()
return results[0]['date']
except Exception as e:
return ''
connection.close()
finally:
connection.close()
def get_sci_sdszf(page_num, type):
url = (f'http://www.shandong.gov.cn/col/col94237/index.html?uid=633233&pageNum={page_num}')
user_Agent = "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/105.0.0.0 Safari/537.36"
headers = {
"Referer": None,
"User-Agent": user_Agent
}
while True:
try:
response = requests.get(url=url, headers=headers)
response.encoding = 'utf-8'
response = response.text
break
except:
print("请求失败,尝试睡眠一会(半小时)")
sleep_time = 60 * 30
time.sleep(sleep_time)
print("睡眠结束,继续运行...")
continue
# 提取日期
da = re.findall(r'<span>\s*(\d{4}-\d{2}-\d{2})\s*</span>', response)
# 提取链接
sci_url = re.findall(r'href="(.*?)"\s+target="_blank"\s+title="', response)
# 提取标题(title 属性)
content = re.findall(r'\s+target="_blank"\s+title="(.*?)"', response)
# return
print(len(da), len(sci_url), len(content))
for i in range(0, len(da)):
print(str(i+1) + ' : ' + da[i][0:10] + ' : '+content[i]+ ' : ' + sci_url[i])
if len(da) != len(sci_url) or len(da) != len(content):
print("数据不完整,跳过插入")
return
new_date = find_new_date()
if not new_date or new_date == '':
new_date = '1970-01-01' # 默认最小日期
connection = connect_to_database()
try:
with connection.cursor() as cursor:
sql = """
INSERT INTO `my_database_test`.`sci_spider`
(`title`, `url`, `date`, `type`, `create_date`)
VALUES (%s, %s, %s, %s, NOW())
"""
count = 0
for i in range(len(da)):
if da[i] > new_date:
count = count + 1
cursor.execute(sql, (content[i], sci_url[i], da[i], type))
connection.commit()
print(f"已成功插入 {count} 条数据")
except Exception as e:
print(f"插入数据失败: {e}")
connection.rollback()
finally:
connection.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
get_sci_sdszf(1, 3)import flask
from flask import request, jsonify
from rescode.constants import ResponseCode
from spider.qiXinSpider import getQiXinCompInfo
'''
flask: web框架,通过flask提供的装饰器@server.route()将普通函数转换为服务
登录接口,需要传url、username、passwd
'''
# 创建一个服务,把当前这个python文件当做一个服务
server = flask.Flask(__name__)
# server.config['JSON_AS_ASCII'] = False
# @server.route()可以将普通函数转变为服务 登录接口的路径、请求方式
@server.route('/python-api/getCompTageFromQiXin', methods=['get', 'post'])
def getCompTageFromQiXin():
try:
# 获取通过url请求传参的数据
httpUrl = request.values.get('httpUrl')
if not httpUrl:
return jsonify(ResponseCode.PARAM_REQUIRED), 400
if 'www.sdxyjq.com:8080' in httpUrl:
httpUrl = httpUrl.replace('www.sdxyjq.com:8080', 'www.sdxyjq.com')
# 调用qiXinSpider.py里面的函数,需要传入
# chrome的路径 D:\\APP\\TestChrome2\\Application\\chrome.exe
# 信用金桥的http链接的url地址
comp_info = getQiXinCompInfo(httpUrl,'D:\\APP\\TestChrome2\\Application\\chrome.exe')
data = {
"httpUrl" : httpUrl,
"qiXinSpider" : comp_info,
"compName":comp_info['baseInfo']['ename']
}
return jsonify({**ResponseCode.SUCCESS, "data": data}), 200
except Exception as e:
# 统一异常捕获
return jsonify(ResponseCode.INTERNAL_ERROR), 500
@server.errorhandler(404)
def not_found(error):
return jsonify({ "code": 404, "message": "接口不存在" }), 404
@server.errorhandler(500)
def internal_error(error):
return jsonify(ResponseCode.INTERNAL_ERROR), 500
if __name__ == '__main__':
server.run(debug=True, port=8888, host='0.0.0.0')爬虫脚本
# -*- encoding:utf-8 -*-
import time
from selenium.webdriver.support.ui import WebDriverWait
from selenium.webdriver.chrome.options import Options
from seleniumwire import webdriver as wiredriver
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
import gzip
import io
import json
# 初始化selenium
def initialize_driver(chromePath: str):
# 配置 Chrome 浏览器选项
chrome_options = Options()
chrome_options.add_argument('--disable-gpu') # 禁用 GPU 加速,确保拦截请求正常
chrome_options.add_argument('--headless') # 不打开浏览器
chrome_options.add_argument('--ignore-certificate-errors') # 忽略证书错误
# 添加指定的浏览器路径
chrome_path = chromePath
chrome_options.binary_location = chrome_path
# 初始化 WebDriver,并传入配置
driver = wiredriver.Chrome(options=chrome_options)
return driver
# 获取启信宝的地址
def get_qixin_url(url):
if 'www.sdxyjq.com:8080' in url:
url = url.replace('www.sdxyjq.com:8080', 'www.sdxyjq.com')
headers = {
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/113.0.0.0 Safari/537.36"
}
response = requests.get(url, headers=headers)
html_content = response.text
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_content, 'html.parser')
iframe = soup.find('iframe')
qiXinUrl = ''
if iframe:
src = iframe.get('src')
qiXinUrl = src
return qiXinUrl
# 格式化请求体
def parse_response_body(response_body_binary):
try:
# 检查数据是否以 gzip 开头
is_gzip = response_body_binary.startswith(b'\\x1f\\x8b')
if is_gzip:
with gzip.GzipFile(fileobj=io.BytesIO(response_body_binary), mode='rb') as f:
return json.loads(f.read().decode('utf-8'))
else:
# print('直接解码为 JSON')
return json.loads(response_body_binary.decode('utf-8'))
except Exception as e:
print(f"格式化请求体失败: {e}")
return None
def extract_response_body(requests, keyword):
for request in requests:
if keyword in request.url:
return request.response.body
return None
def getQiXinCompInfo(url:str,chromePath:str):
try:
# 初始化浏览器
driver = initialize_driver(chromePath)
# 访问启信宝的网页
driver.get(get_qixin_url(url))
time.sleep(3)
# 使用 WebDriverWait 等待页面加载完成之后继续操作,等待时间根据网络情况进行调整
wait = WebDriverWait(driver, 30)# 超时时间30s
# 等待页面的 document.readyState 变为 "complete"
wait.until(lambda driver: driver.execute_script("return document.readyState") == "complete")
# 获取所有拦截的请求
requests = driver.requests
# 获取企业的标签信息 getEntLabel
res_getEntLabel = extract_response_body(requests, 'getEntLabel')
if res_getEntLabel is not None:
res_getEntLabel = parse_response_body(res_getEntLabel)
else:
res_getEntLabel =''
# 获取企业地址信息 getGeocode
res_getGeocode = extract_response_body(requests, 'getGeocode')
if res_getGeocode is not None:
res_getGeocode = parse_response_body(res_getGeocode)
else:
res_getGeocode = ''
# 获取企业的工商信息 getEntBasicInfoNew
res_getEntBasicInfoNew = extract_response_body(requests,'getEntBasicInfoNew')
if res_getEntBasicInfoNew is not None:
res_getEntBasicInfoNew = parse_response_body(res_getEntBasicInfoNew)
else:
res_getEntBasicInfoNew = ''
return {
'baseInfo': res_getEntBasicInfoNew,
'tagInfo': res_getEntLabel,
'addressInfo': res_getGeocode,
}
finally:
# 关闭浏览器
driver.quit()Flask 是什么?
Flask 是一个用 Python 编写的轻量级 Web 框架 ,它为构建 Web 应用程序和 RESTful API 提供了灵活的基础。Flask 的设计哲学是“简洁和可扩展”,它没有捆绑任何数据库或 ORM(对象关系映射)工具,开发者可以根据需求自由选择技术栈。
Flask 的核心特点
轻量级与灵活性 :
- 没有强制性的数据库或 ORM,开发者可以自由选择技术(如 SQLite、MySQL、MongoDB 等)。
- 不依赖模板引擎,默认提供简单模板,也可以替换为其他引擎(如 Jinja2)。
路由系统 :
- 通过装饰器(Decorator)将 URL 路径映射到 Python 函数
扩展性 :
通过第三方扩展(Extensions)增强功能,例如:
- Flask-SQLAlchemy :数据库操作。
- Flask-RESTful :快速构建 RESTful API。
- Flask-Login :用户认证。
- Flask-JWT :基于 JWT 的身份验证。
开发友好 :
- 内置调试模式(Debug Mode),实时反映代码修改。
- 支持单元测试和集成测试。
社区支持 :
- 拥有活跃的开源社区和丰富的文档,适合快速开发和学习。
Flask 的典型应用场景
小型 Web 应用 :
- 适合快速开发个人博客、仪表盘、内部工具等。
RESTful API 开发 :
- 构建数据接口(如 JSON API),常用于前后端分离项目。
微服务架构 :
- 由于轻量级特性,适合构建独立的微服务模块。
学习 Web 开发 :
- 简单的 API 和路由设计使其成为学习 Web 开发的理想工具。
Flask 与 Django 的对比
| 特性 | FLASK | DJANGO |
|---|---|---|
| 设计理念 | 轻量级、灵活,最小功能集 | 重量级、全功能, batteries-included |
| 默认组件 | 无 ORM、模板引擎(可选) | 内置 ORM(Django ORM)、模板引擎 |
| 学习曲线 | 低(简单直接) | 高(功能丰富但复杂) |
| 适用场景 | 小型项目、API、需要高度控制的场景 | 企业级大型项目、快速全栈开发 |
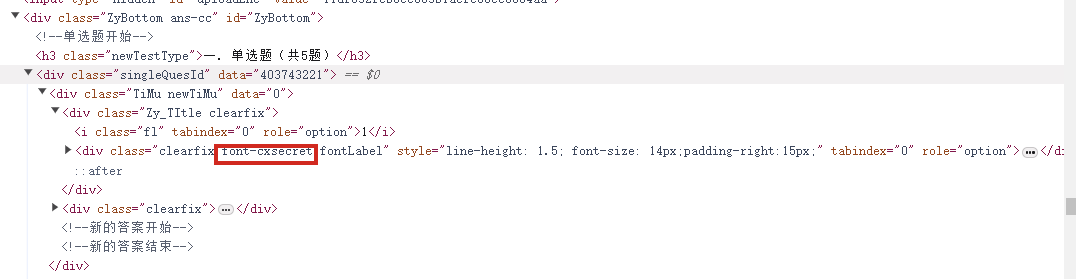
搜索页面和这个相关的从而定位到引入文件
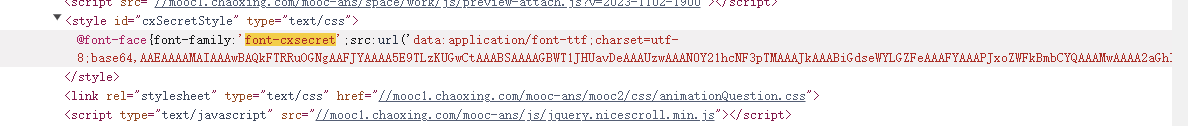
查找,一眼Base64编码的字体文件,通过这个编码数据解码获得原字体文件
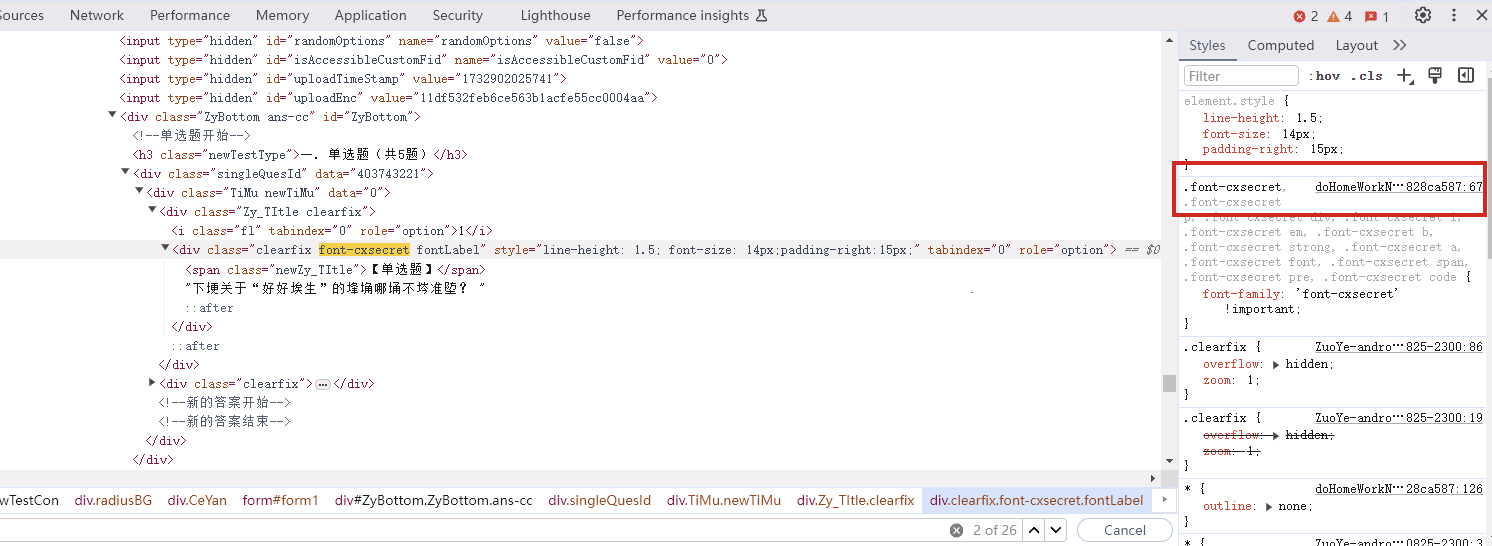
找到之后进去查看
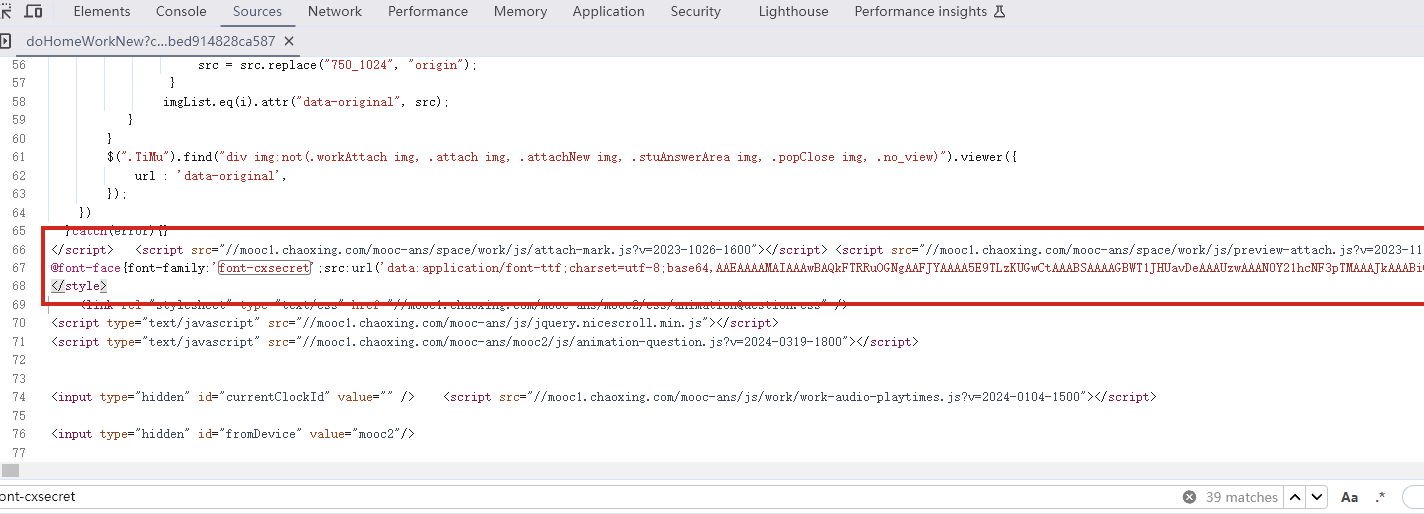
找到了,把里面内容复制下来,掐头去尾,是这样的数据
编写脚本进行解码,引号内填写base64编码数据去掉data:application/font-ttf;charset=utf-8;base64,的开头声明"
import base64
# Base64编码的字符串
base64_string = "这里填写base64编码数据去掉data:application/font-ttf;charset=utf-8;base64,的开头声明"
# 解码Base64字符串
decoded_data = base64.b64decode(base64_string)
# 保存为.ttf文件
with open("chaoxing_font.ttf", "wb") as f:
f.write(decoded_data)获得到base64的ttf文件结果
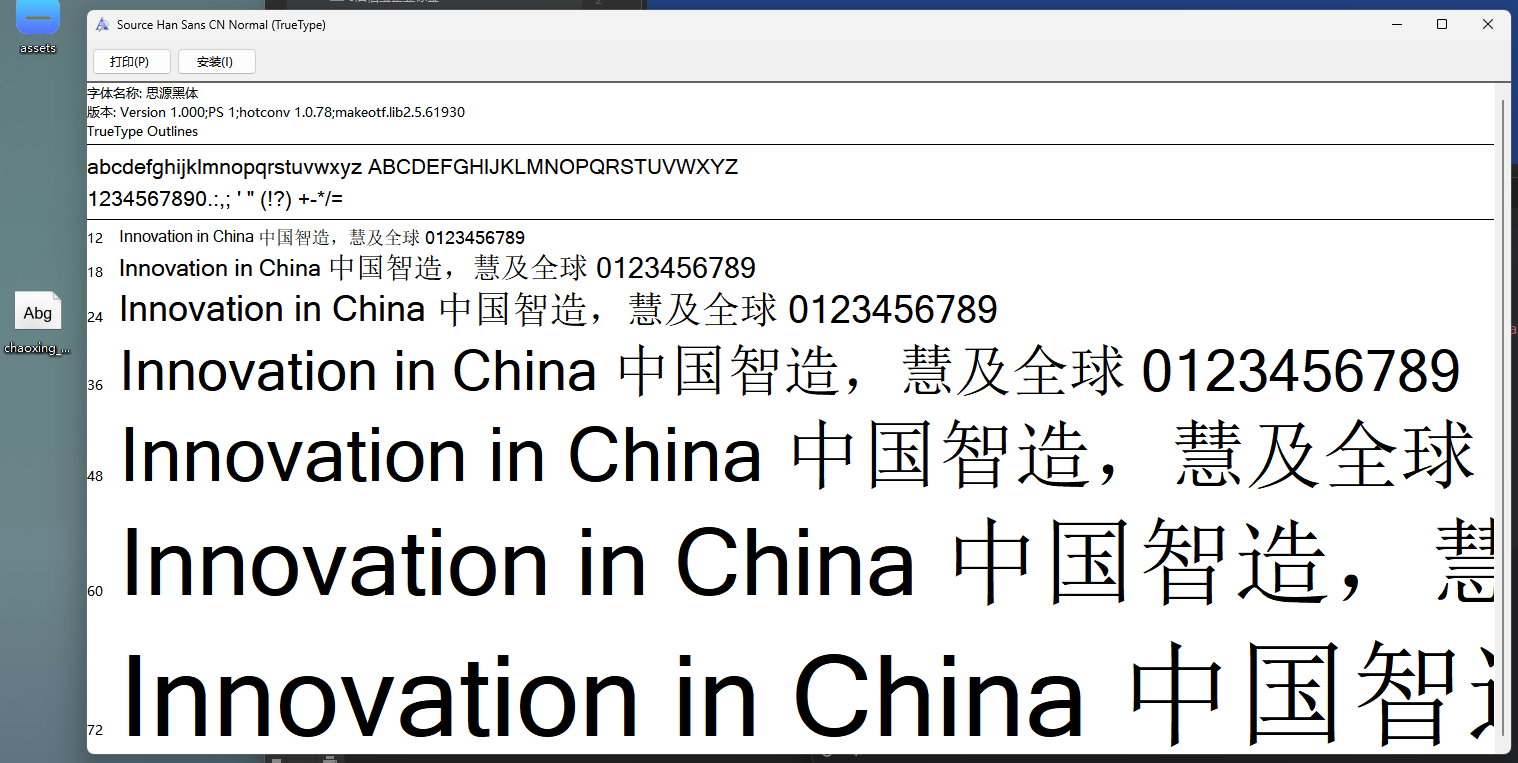
使用字体查看器查看字体 https://www.bejson.com/ui/font/
接下来将ttf文件转换成xml文件(python需要安装fontTools)
from fontTools.ttLib import TTFont
# TTF 文件路径
ttf_path = r"D:\UserData\Desktop\chaoxing_font.ttf"
xml_output_path = r"D:\UserData\Desktop\chaoxing_font.xml"
# 加载字体文件
font = TTFont(ttf_path)
# 保存为 XML 文件
font.saveXML(xml_output_path)
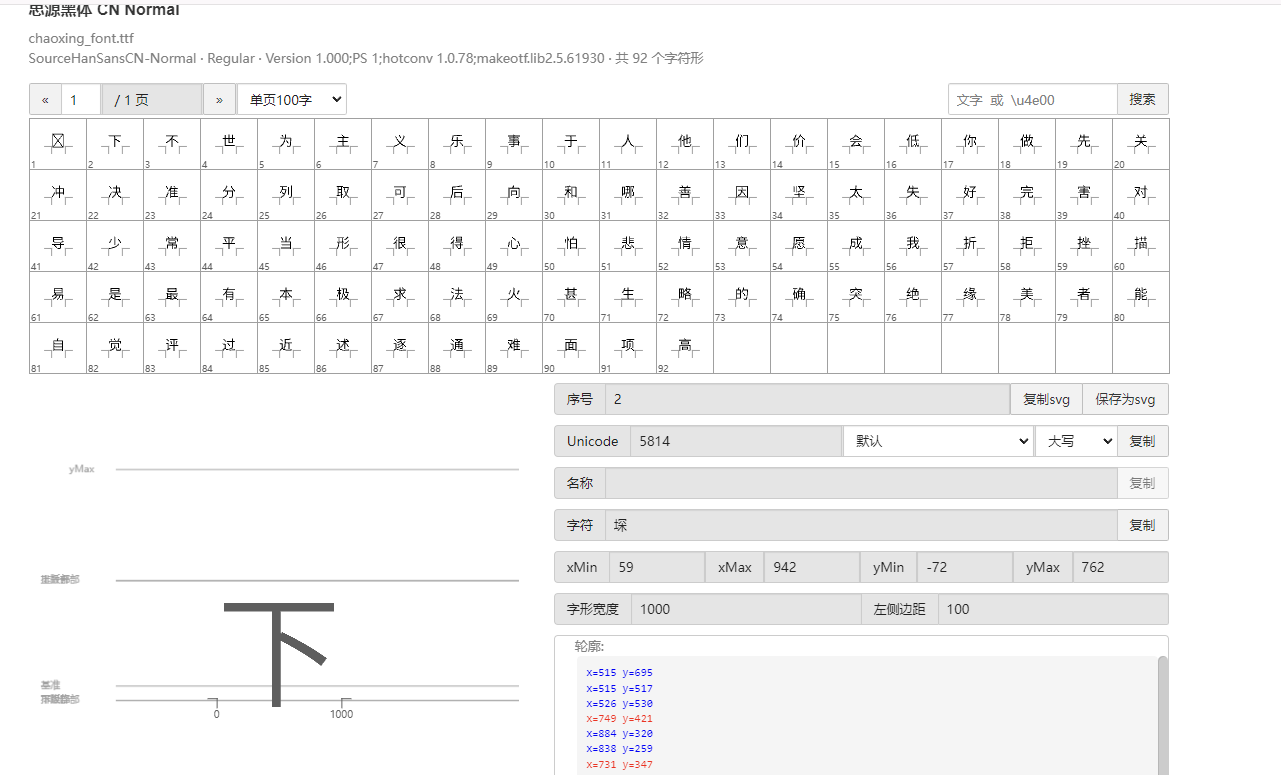
print(f"解析完毕")抽选字体对比一下映射结果对不对(超星的加密是修改了此字体图元数据,显示成未加密的字)
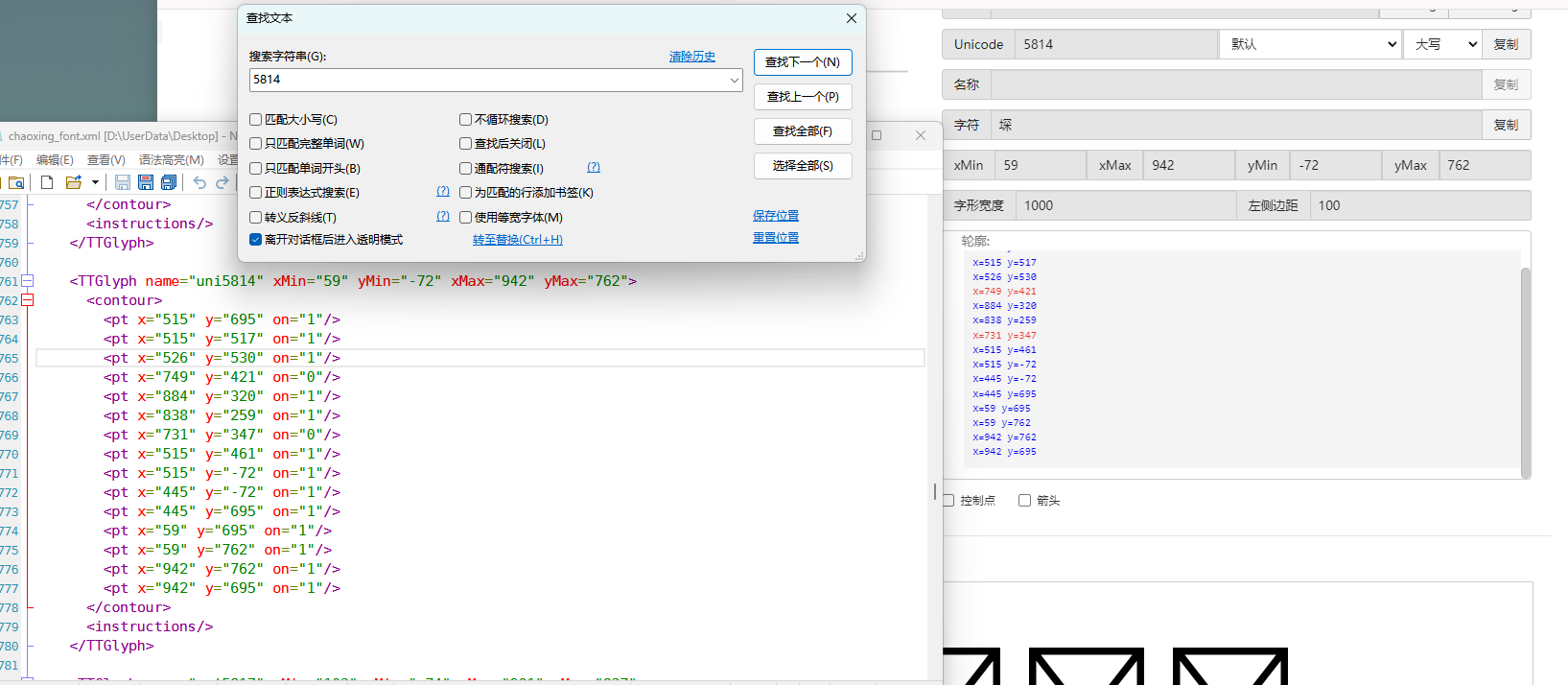
下载原来的字体文件(非超星加密后的文件)
源字体文件对应
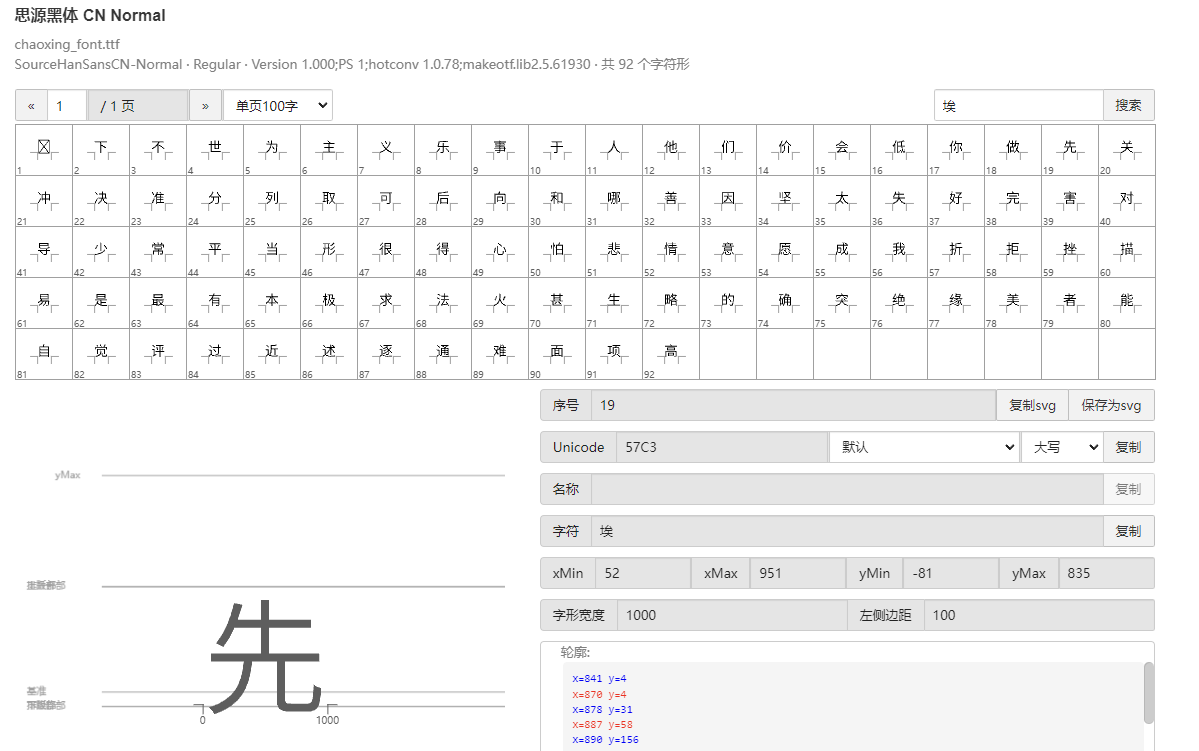
超星加密后字体
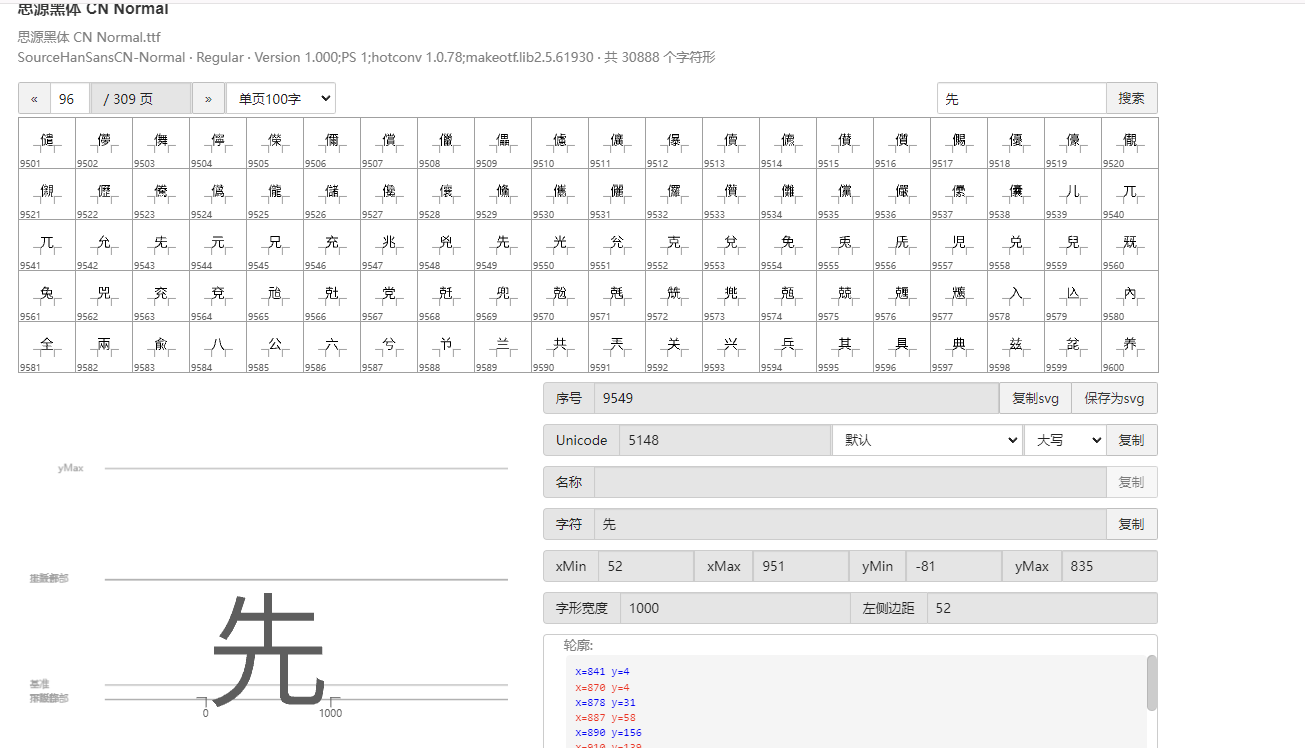
也就是说原来的5148对应着57C3
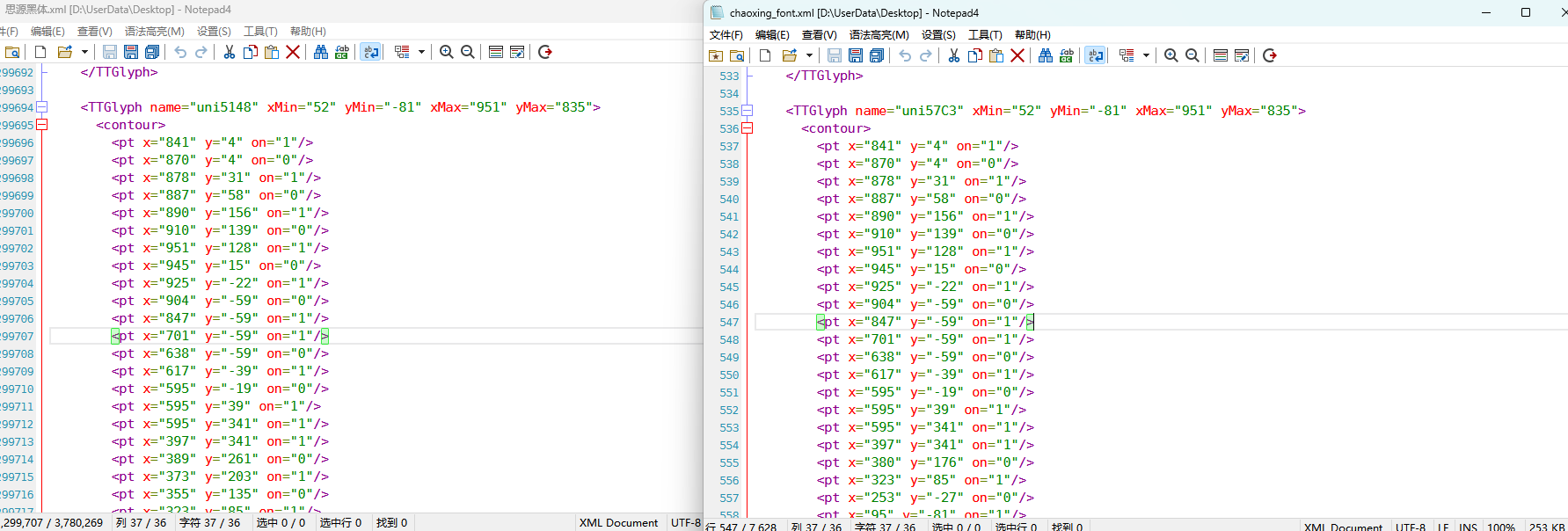
编写对比代码进行测试
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import hashlib
import json
def parse_glyphs(file_path):
"""
解析字体文件中的 TTGlyph 信息
"""
tree = ET.parse(file_path)
root = tree.getroot()
glyphs = {}
for glyph in root.findall(".//TTGlyph"):
name = glyph.get("name")
points = []
for pt in glyph.findall(".//pt"):
x = pt.get("x")
y = pt.get("y")
on = pt.get("on")
points.append(f"{x}{y}{on}")
# 生成轮廓的唯一哈希值
hash_value = hashlib.md5("".join(points).encode('utf-8')).hexdigest()
# 截取哈希值的 25-32 位来作为唯一标识
truncated_hash = hash_value[24:32]
glyphs[truncated_hash] = name # 使用截取后的哈希值作为键
return glyphs
def get_unicode_character(name):
"""
根据 glyph 名称(如 uni5148)获取对应汉字
"""
if name.startswith("uni"):
try:
unicode_value = int(name[3:], 16)
return chr(unicode_value)
except ValueError:
return None
return None
def build_mapping(xml_old_path, xml_cx_path):
"""
建立思源黑体和超星字体的对照关系
"""
old_glyphs = parse_glyphs(xml_old_path)
print(len(old_glyphs))
cx_glyphs = parse_glyphs(xml_cx_path)
print(len(cx_glyphs))
mapping = []
for cx_hash, cx_name in cx_glyphs.items():
if cx_hash in old_glyphs:
old_name = old_glyphs[cx_hash]
character = get_unicode_character(old_name)
if character: # 确保是有效汉字
mapping.append({
"chaoxing": cx_name,
"si_yuan": {
"siyuan_name": old_name,
"siyuan_name_value": character
}
})
return mapping
if __name__ == "__main__":
xml_old_path = r"D:\UserData\Desktop\思源黑体.xml"
xml_cx_path = r"D:\UserData\Desktop\chaoxing_font.xml"
result = build_mapping(xml_old_path, xml_cx_path)
# 输出到文件
with open("glyph_mapping.json", "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
json.dump(result, f, ensure_ascii=False, indent=4)
# 打印部分结果
# print(json.dumps(result[:5], ensure_ascii=False, indent=4))生成结果
[
{
"chaoxing": "uni57C2",
"si_yuan": {
"siyuan_name": "uni2FAF",
"siyuan_name_value": "⾯"
}
},
{
"chaoxing": "uni57E0",
"si_yuan": {
"siyuan_name": "uni5584",
"siyuan_name_value": "善"
}
},
{
"chaoxing": "uni580F",
"si_yuan": {
"siyuan_name": "uni4E16",
"siyuan_name_value": "世"
}
},
{
"chaoxing": "uni581D",
"si_yuan": {
"siyuan_name": "uni5BB3",
"siyuan_name_value": "害"
}
},
{
"chaoxing": "uni900B",
"si_yuan": {
"siyuan_name": "uni2F83",
"siyuan_name_value": "⾃"
}
}
]我采用的字符串是
超星:下埂关于“好好埃生”的埄埆哪埇不埁准埅?
思源:下面关于“好好先生”的描述哪项不太准确?
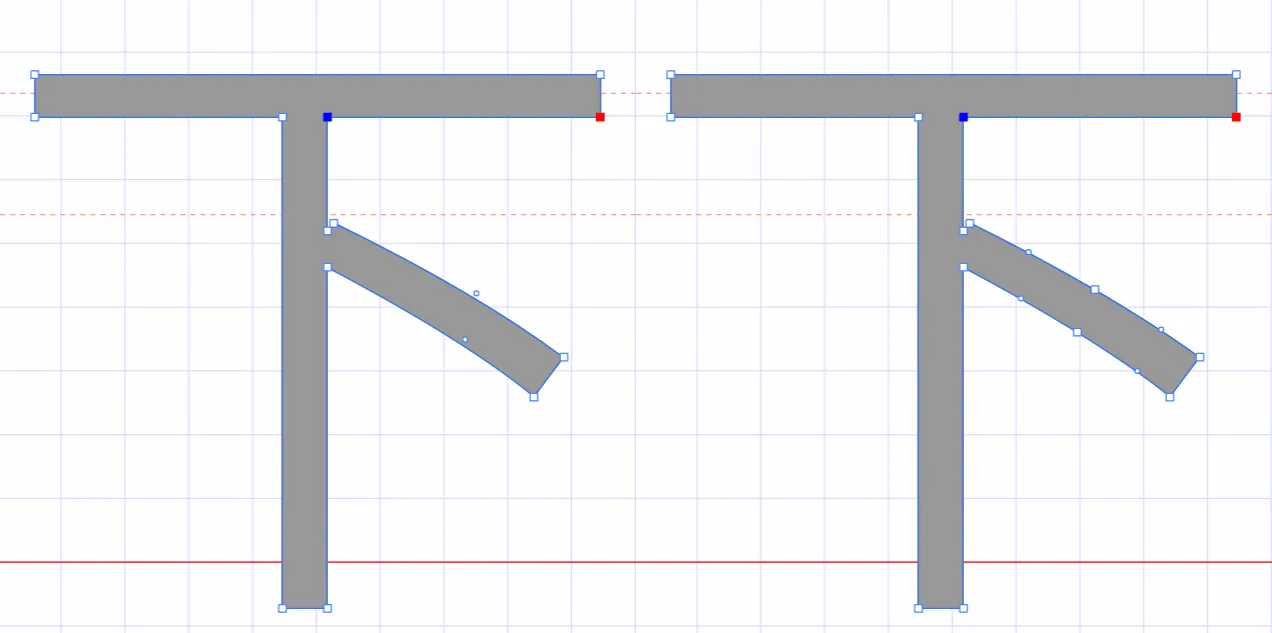
结合对照表显示,发现字体字形数据并对不上,查看字体数据,针对“下“字进行分析,发现两边结果并对不上,结果是超星对于字体字形进行了更改,并不是简单的对比字符哈希值就可以对比出来的了。

查看对比效果
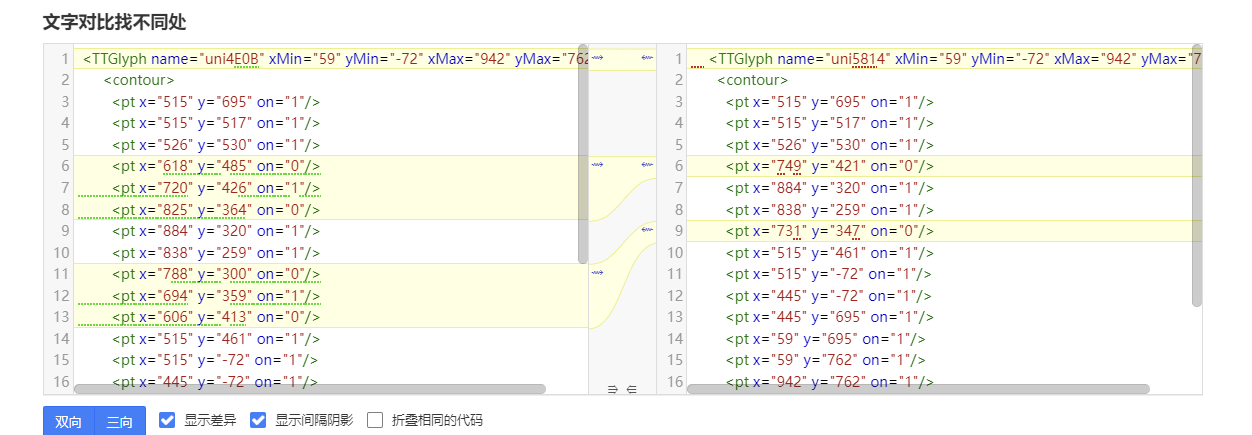
左侧为原版字体,右侧为学习通字体
百度到” I Am I“大佬的文章”从学习通复制文字乱码看前端版权保护“找到一定的思路是假设字符的边距是唯一的,好的,那么我们就拼接边距距离。得出以下代码
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import hashlib
import json
def parse_glyphs(file_path):
"""
解析字体文件中的 TTGlyph 信息,使用 xMin, yMin, xMax, yMax 作为唯一标识
"""
tree = ET.parse(file_path)
root = tree.getroot()
glyphs = {}
for glyph in root.findall(".//TTGlyph"):
name = glyph.get("name")
# 获取 xMin, yMin, xMax, yMax
xMin = glyph.get("xMin")
yMin = glyph.get("yMin")
xMax = glyph.get("xMax")
yMax = glyph.get("yMax")
# 使用这四个值拼接成唯一标识符
if xMin and yMin and xMax and yMax:
unique_key = f"{xMin}{yMin}{xMax}{yMax}"
glyphs[unique_key] = name # 用四个边界值作为唯一键,值为glyph名称
return glyphs
# def parse_glyphs(file_path):
# """
# 解析字体文件中的 TTGlyph 信息
# """
# tree = ET.parse(file_path)
# root = tree.getroot()
#
# glyphs = {}
#
# for glyph in root.findall(".//TTGlyph"):
# name = glyph.get("name")
# points = []
# for pt in glyph.findall(".//pt"):
# x = pt.get("x")
# y = pt.get("y")
# on = pt.get("on")
# points.append(f"{x}{y}{on}")
#
# # 生成轮廓的唯一哈希值
# hash_value = hashlib.md5("".join(points).encode('utf-8')).hexdigest()
# glyphs[hash_value] = name # 哈希值对应 glyph 名称
#
# return glyphs
def get_unicode_character(name):
"""
根据 glyph 名称(如 uni5148)获取对应汉字
"""
if name.startswith("uni"):
try:
unicode_value = int(name[3:], 16)
return chr(unicode_value)
except ValueError:
return None
return None
def build_mapping(xml_old_path, xml_cx_path):
"""
建立思源黑体和超星字体的对照关系
"""
old_glyphs = parse_glyphs(xml_old_path)
# print(len(old_glyphs))
cx_glyphs = parse_glyphs(xml_cx_path)
# print(len(cx_glyphs))
# print(cx_glyphs)
mapping = []
for cx_hash, cx_name in cx_glyphs.items():
if cx_hash in old_glyphs:
old_name = old_glyphs[cx_hash]
character = get_unicode_character(old_name)
if cx_name == 'uni5814':
print(cx_hash)
print(old_name)
if character: # 确保是有效汉字
mapping.append({
"chaoxing": cx_name,
"si_yuan" : {
"siyuan_name": old_name,
"siyuan_name_value": character
}
})
return mapping
if __name__ == "__main__":
xml_old_path = r"D:\UserData\Desktop\思源黑体.xml"
xml_cx_path = r"D:\UserData\Desktop\chaoxing_font.xml"
result = build_mapping(xml_old_path, xml_cx_path)
# 输出到文件
with open("glyph_mapping.json", "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
json.dump(result, f, ensure_ascii=False, indent=4)
# 打印部分结果
# print(json.dumps(result[:5], ensure_ascii=False, indent=4))再通过匹配结果进行查看数据
import json
# 读取json
def load_mapping(file_path):
with open(file_path, "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
return json.load(f)
# 获取字符对应的 uni 名称
def get_uni_name(character, mapping):
unicode_name = f"uni{ord(character):X}"
# print(unicode_name)
for entry in mapping:
if entry["chaoxing"] == unicode_name:
return entry
return None
# 解析字符串
def parse_code(code, mapping):
result = []
for char in code:
mapping_entry = get_uni_name(char, mapping)
if mapping_entry:
result.append({
"char": char,
"message": mapping_entry["si_yuan"]['siyuan_name_value']
})
else:
result.append({
"char": char,
"message": char
})
return result
# 测试代码
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 读取字形映射
glyph_mapping_file = "glyph_mapping.json"
mapping = load_mapping(glyph_mapping_file)
# 示例字符串
code = '下埂关于“好好埃生”的埄埆哪埇不埁准埅?'
# 解析字符串
parsed_result = parse_code(code, mapping)
# 输出解析结果
# for item in parsed_result:
# print(item)
print(f'超星字体:{code}')
siyuan_font = ''.join([item['message'] for item in parsed_result])
print(f'思源字体:{siyuan_font}')得出结果
超星字体:下埂关于“好好埃生”的埄埆哪埇不埁准埅?
思源字体:下⾯关于“好好先生”的描述哪项不太准确?在大佬的测试中,是可以确定90%左右的字符数据的。如果您不想看了,到这里就可以了,基本满足所有的效果了。
然后由于最近领导给我一些任务就是比较两个字符串的相似度,通过这个启发就想通过xy向量计算字符字形的相似度。得出以下代码,首先针对”下”字进行数据测试
归一化:将所有点归一化到相同的尺度。(如果不归一,DTW有要求长度一样,会报错)
归一化点集(Normalization of points)是指将原始点集中的每个点的坐标变换到一个特定的标准范围,以消除由于坐标范围不同而引起的差异,从而使得数据的比较更加公正和一致。具体而言,在这段代码中,归一化的目标是将每个点的坐标缩放到
[0, 1]的范围内。为什么要进行归一化?
在计算点集之间的相似度时(如使用动态时间规整 DTW),不同的点集可能有不同的坐标范围或单位。如果不进行归一化,可能会因为坐标差异较大,导致计算出的相似度偏差较大。归一化的过程能够消除这种影响,让两个点集具有相同的尺度,从而公平地比较它们之间的相似性。
举个例子:
假设有一个点集:
points = [(10, 20), (30, 40), (50, 60), (70, 80)]经过归一化处理后:
- 最小值:
min_x = 10,min_y = 20 - 最大值:
max_x = 70,max_y = 80
每个点将会变成:
(10, 20)变成(0, 0)(30, 40)变成(0.333, 0.333)(50, 60)变成(0.666, 0.666)(70, 80)变成(1, 1)
最终,这些点就会被归一化到
[0, 1]的范围内,这样它们的尺度是一致的,适合用于后续的相似度计算。归一化的目的是消除不同点集之间的坐标尺度差异,使得不同的点集可以在相同的尺度下进行比较。通过这种方式,我们可以更加公平地计算它们之间的相似度,而不会因为坐标的差异导致错误的比较结果。- 最小值:
使用DTW进行点对齐:保持原有的DTW对齐方法。
这里计算两个点集的相似度分数,通过DTW距离计算得出一个0~1的相似度分数。1完全相似,0完全不一样。
函数使用
fastdtw函数计算归一化后的两个点集之间的 DTW 距离。DTW 是一种衡量两组时间序列相似度的算法,常用于处理不等长、速度不同的序列数据。在这里,它也可以用于比较两个二维点集的相似度。- 计算相似度:基于对齐后的点集计算相似度。
import numpy as np
from fastdtw import fastdtw
from scipy.spatial.distance import euclidean
# 假设我们已经有了两个字形的数据
ttglyph_superstar = [
(515, 695), (515, 517), (526, 530), (749, 421), (884, 320),
(838, 259), (731, 347), (515, 461), (515, -72), (445, -72),
(445, 695), (59, 695), (59, 762), (942, 762), (942, 695)
]
ttglyph_sourcehan = [
(515, 695), (515, 517), (526, 530), (618, 485), (720, 426),
(825, 364), (884, 320), (838, 259), (788, 300), (694, 359),
(606, 413), (515, 461), (515, -72), (445, -72), (445, 695),
(59, 695), (59, 762), (942, 762), (942, 695)
]
# 转换为numpy数组
points1 = np.array(ttglyph_superstar)
points2 = np.array(ttglyph_sourcehan)
def normalize_points(points):
"""
归一化点集
"""
if len(points) == 0: # 检查点集是否为空
return []
points = np.array(points) # 将点集转换为NumPy数组
min_x, min_y = np.min(points, axis=0)
max_x, max_y = np.max(points, axis=0)
# 防止除以零
if max_x == min_x:
max_x = min_x + 1
if max_y == min_y:
max_y = min_y + 1
normalized_points = (points - [min_x, min_y]) / [max_x - min_x, max_y - min_y]
return normalized_points
def calculate_similarity(points1, points2):
"""
使用DTW计算两个点集之间的相似度
"""
points1_normalized = normalize_points(points1)
points2_normalized = normalize_points(points2)
if len(points1_normalized) == 0 or len(points2_normalized) == 0:
return 0.0 # 如果任一点集为空,相似度为0
#distance 是 DTW 算法计算出来的总距离,表示两个点集的整体差异。
#path 是 DTW 算法找到的最佳对齐路径,指示了如何从 points1 映射到 points2。
distance, path = fastdtw(points1_normalized, points2_normalized, dist=euclidean)
# DTW 算法会计算出一组“对齐”路径,通过这个路径可以重新排列两个点集,使它们更好地对齐。根据 path 的内容,分别从 points1_normalized 和 points2_normalized 中提取对齐后的点集。
aligned_points1 = [points1_normalized[i] for i, _ in path]
aligned_points2 = [points2_normalized[j] for _, j in path]
# 计算对齐点之间的欧几里得距离,在最佳对齐下,每对点之间的差异。np.linalg.norm 计算的是两点之间的欧几里得距离
distances = [np.linalg.norm(np.array(p1) - np.array(p2)) for p1, p2 in zip(aligned_points1, aligned_points2)]
# 算出所有欧氏距离去平局书,得出平均欧氏距距离
average_distance = np.mean(distances)
similarity_score = 1 / (1 + average_distance)
return similarity_score
print(f"Similarity score: {calculate_similarity(points2,points1)}")得出结果
Similarity score: 0.975700703557036发现相似度还是很高的,这里是需要忽略字体的风格的,和笔画的这些。
好的,可以通过这种相似度算法去核对超星字体对应的元数据了。
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import json
import numpy as np
from fastdtw import fastdtw
from scipy.spatial.distance import euclidean
from tqdm import tqdm
def parse_glyphs(file_path):
"""
解析字体文件中的 TTGlyph 信息
"""
tree = ET.parse(file_path)
root = tree.getroot()
glyphs = {}
for glyph in root.findall(".//TTGlyph"):
name = glyph.get("name")
points = []
for pt in glyph.findall(".//pt"):
x = int(pt.get("x"))
y = int(pt.get("y"))
on = int(pt.get("on", 0)) # 默认值为0,如果不存在则设为0
points.append((x, y))
# 将点集转换为字符串,作为字典的键
key = str(points)
glyphs[key] = name
return glyphs
def get_unicode_character(name):
"""
根据 glyph 名称(如 uni5148)获取对应汉字
"""
if name.startswith("uni"):
try:
unicode_value = int(name[3:], 16)
return chr(unicode_value)
except ValueError:
return None
return None
def normalize_points(points):
"""
归一化点集
"""
if not points: # 检查点集是否为空
return []
points = np.array(points) # 将点集转换为NumPy数组
min_x, min_y = np.min(points, axis=0)
max_x, max_y = np.max(points, axis=0)
# 防止除以零
if max_x == min_x:
max_x = min_x + 1
if max_y == min_y:
max_y = min_y + 1
normalized_points = (points - [min_x, min_y]) / [max_x - min_x, max_y - min_y]
return normalized_points
def calculate_similarity(points1, points2):
"""
使用DTW计算两个点集之间的相似度
"""
points1_normalized = normalize_points(points1)
points2_normalized = normalize_points(points2)
if len(points1_normalized) == 0 or len(points2_normalized) == 0:
return 0.0 # 如果任一点集为空,相似度为0
distance, path = fastdtw(points1_normalized, points2_normalized, dist=euclidean)
aligned_points1 = [points1_normalized[i] for i, _ in path]
aligned_points2 = [points2_normalized[j] for _, j in path]
distances = [np.linalg.norm(np.array(p1) - np.array(p2)) for p1, p2 in zip(aligned_points1, aligned_points2)]
average_distance = np.mean(distances)
similarity_score = 1 / (1 + average_distance)
return similarity_score
def build_mapping(xml_old_path, xml_cx_path):
"""
建立思源黑体和超星字体的对照关系
"""
old_glyphs = parse_glyphs(xml_old_path)
print(f'思源字体:{len(old_glyphs)}')
cx_glyphs = parse_glyphs(xml_cx_path)
print(f'超星字体:{len(cx_glyphs)}')
mapping = []
total_combinations = len(old_glyphs) * len(cx_glyphs)
with tqdm(total=total_combinations, desc="Processing") as pbar:
for old_key, old_name in old_glyphs.items():
for cx_key, cx_name in cx_glyphs.items():
similarity = calculate_similarity(eval(old_key), eval(cx_key))
if similarity >= 0.9:
mapping.append({
"chaoxing": {
"cx_name": cx_name,
"cx_character": get_unicode_character(cx_name)
},
"si_yuan": {
"sy_name": old_name,
"sy_character": get_unicode_character(old_name)
},
"similarity": similarity
})
pbar.update(1)
return mapping
if __name__ == "__main__":
xml_old_path = r"D:\UserData\Desktop\思源黑体.xml"
xml_cx_path = r"D:\UserData\Desktop\chaoxing_font.xml"
result = build_mapping(xml_old_path, xml_cx_path)
# 输出到文件
with open("glyph_mapping2.json", "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
json.dump(result, f, ensure_ascii=False, indent=4)
# print(json.dumps(result[:5], ensure_ascii=False, indent=4))但是运行效果不如人意
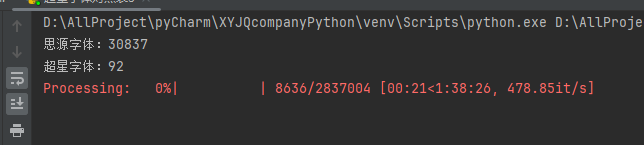
这么长的时间肯定是不能忍的,所有采用多线程的处理方式,cpu就应该忙起来了。
from concurrent.futures import ProcessPoolExecutor, as_completed
import json
import numpy as np
from fastdtw import fastdtw
from scipy.spatial.distance import euclidean
from tqdm import tqdm
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
# 其他函数不变,保持之前的代码
def calculate_similarity(points1, points2):
"""
使用DTW计算两个点集之间的相似度
"""
points1_normalized = normalize_points(points1)
points2_normalized = normalize_points(points2)
if len(points1_normalized) == 0 or len(points2_normalized) == 0:
return 0.0 # 如果任一点集为空,相似度为0
distance, path = fastdtw(points1_normalized, points2_normalized, dist=euclidean)
aligned_points1 = [points1_normalized[i] for i, _ in path]
aligned_points2 = [points2_normalized[j] for _, j in path]
distances = [np.linalg.norm(np.array(p1) - np.array(p2)) for p1, p2 in zip(aligned_points1, aligned_points2)]
average_distance = np.mean(distances)
similarity_score = 1 / (1 + average_distance)
return similarity_score
def normalize_points(points):
"""
归一化点集
"""
if not points: # 检查点集是否为空
return []
points = np.array(points) # 将点集转换为NumPy数组
min_x, min_y = np.min(points, axis=0)
max_x, max_y = np.max(points, axis=0)
# 防止除以零
if max_x == min_x:
max_x = min_x + 1
if max_y == min_y:
max_y = min_y + 1
normalized_points = (points - [min_x, min_y]) / [max_x - min_x, max_y - min_y]
return normalized_points
def parallel_calculate_similarity(old_key, old_name, cx_glyphs):
"""
并行计算相似度
"""
results = []
for cx_key, cx_name in cx_glyphs.items():
similarity = calculate_similarity(eval(old_key), eval(cx_key))
if similarity >= 0.9:
results.append({
"chaoxing": {
"cx_name": cx_name,
"cx_character": get_unicode_character(cx_name)
},
"si_yuan": {
"sy_name": old_name,
"sy_character": get_unicode_character(old_name)
},
"similarity": similarity
})
return results
def get_unicode_character(name):
"""
根据 glyph 名称(如 uni5148)获取对应汉字
"""
if name.startswith("uni"):
try:
unicode_value = int(name[3:], 16)
return chr(unicode_value)
except ValueError:
return None
return None
def parse_glyphs(file_path):
"""
解析字体文件中的 TTGlyph 信息
"""
tree = ET.parse(file_path)
root = tree.getroot()
glyphs = {}
for glyph in root.findall(".//TTGlyph"):
name = glyph.get("name")
points = []
for pt in glyph.findall(".//pt"):
x = int(pt.get("x"))
y = int(pt.get("y"))
on = int(pt.get("on", 0)) # 默认值为0,如果不存在则设为0
points.append((x, y))
# 将点集转换为字符串,作为字典的键
key = str(points)
glyphs[key] = name
return glyphs
def build_mapping_parallel(xml_old_path, xml_cx_path):
"""
并行建立思源黑体和超星字体的对照关系
"""
old_glyphs = parse_glyphs(xml_old_path)
print(f'思源字体:{len(old_glyphs)}')
cx_glyphs = parse_glyphs(xml_cx_path)
print(f'超星字体:{len(cx_glyphs)}')
mapping = []
# 使用进程池进行并行处理
with ProcessPoolExecutor() as executor:
futures = []
# 为每个思源字体字形提交任务
for old_key, old_name in old_glyphs.items():
futures.append(executor.submit(parallel_calculate_similarity, old_key, old_name, cx_glyphs))
# 通过 as_completed 获取计算结果
for future in tqdm(as_completed(futures), total=len(futures), desc="Processing"):
mapping.extend(future.result())
return mapping
if __name__ == "__main__":
xml_old_path = r"D:\UserData\Desktop\思源黑体.xml"
xml_cx_path = r"D:\UserData\Desktop\chaoxing_font.xml"
result = build_mapping_parallel(xml_old_path, xml_cx_path)
# 输出到文件
with open("glyph_mapping_parallel.json", "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
json.dump(result, f, ensure_ascii=False, indent=4)
# 打印部分结果
print(json.dumps(result[:5], ensure_ascii=False, indent=4))这样处理时间来到了半小时(不过cpu要满了),因为我要求把大于0.9的数据全弄出来了,所以会有很多重复的字形数据。这里还需要取出相似度最高的那一个字形数据。
import json
# 读取保存的结果文件并生成包含所有相似度最高数据的 high.json 文件
def find_most_similar_for_all(result_file="glyph_mapping_parallel.json", output_file="high.json"):
# 读取 JSON 数据
with open(result_file, "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
data = json.load(f)
# 用于存储每个 chaoxing 对应的最相似的 si_yuan 对照项
highest_similarity_entries = {}
# 遍历所有条目,找出每个 chaoxing 字符对应的最相似的 si_yuan 对照项
for entry in data:
cx_name = entry["chaoxing"]["cx_name"]
similarity = entry["similarity"]
# 如果该 cx_name 没有出现过,或者当前相似度更高,更新最相似的条目
if cx_name not in highest_similarity_entries or similarity > highest_similarity_entries[cx_name]["similarity"]:
highest_similarity_entries[cx_name] = entry
# print(len(highest_similarity_entries))
# 将结果保存到 high.json 文件
with open(output_file, "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
json.dump(list(highest_similarity_entries.values()), f, ensure_ascii=False, indent=4)
print(f"已将结果保存到 {output_file}")
# 调用函数,生成 high.json 文件
find_most_similar_for_all()至此,我们以及彻底完成了映射表的制作。然后拿数据跑一下进行测试
import json
# 读取 high.json 文件并加载数据
def load_high_json(file_path="high.json"):
with open(file_path, "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
return json.load(f)
# 根据 high.json 匹配字符串中的每个字符,返回结果字符串
def match_string_with_high_json(code, high_json_data):
result = []
for char in code:
# 遍历 high.json 中的所有项,查找匹配的 cx_character
matched = False
for entry in high_json_data:
if entry["chaoxing"]["cx_character"] == char:
# 根据需要将匹配的结果拼接成字符串
result.append(entry["si_yuan"]["sy_character"]) # 使用 si_yuan 对应的字符
matched = True
break
if not matched:
# 如果没有找到匹配的项,保留原字符
result.append(char)
# 将匹配结果列表合并成一个字符串
return ''.join(result)
# 示例字符串
code = '下埂关于“好好埃生”的埄埆哪埇不埁准埅?'
# 加载 high.json 数据
high_json_data = load_high_json()
# 匹配字符串
result_string = match_string_with_high_json(code, high_json_data)
print(f'超星字体:{code}')
print(f'思源字体:{result_string}')得出结果
超星字体:下埂关于“好好埃生”的埄埆哪埇不埁准埅?
思源字体:下⾯关于“好好先生”的描述哪项不太准确?好的,已经可以了,这里关于超星字体的时候,有个疑问就是为什么每个页面加载页面的字体,不能拿到全部的,我这个不知道咋弄,很困扰我,希望有大佬可以帮忙解释一下。
至此,文章彻底结束。
参考文章:
关于超星学习通网页版字体加密分析 :https://www.52pojie.cn/thread-1631357-4-1.html
从学习通复制文字乱码看前端版权保护:https://5ime.cn/xxt_font.html
]]>import os
import re
# 常见图片格式
IMAGE_PATTERN = re.compile(r'!\[.*?\]\((.*?\.(?:png|jpe?g|gif|bmp|svg))\)', re.IGNORECASE)
# 路径
base_path = r"D:\oneDrive\Note\blog\source"
def find_md_with_images(base_path):
md_files_with_images = []
for root, _, files in os.walk(base_path):
for file in files:
if file.endswith('.md'):
file_path = os.path.join(root, file)
# 检查文件内容是否包含图片
with open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
content = f.read()
if IMAGE_PATTERN.search(content):
md_files_with_images.append(file_path)
return md_files_with_images
# 查找并打印结果
if __name__ == "__main__":
result = find_md_with_images(base_path)
if result:
print(f"包含图片的Markdown文件({len(result)}个):")
for md_file in result:
print(md_file)
else:
print("未找到包含图片的Markdown文件。")DAIL-SQL这个开源模型调试的。研究生说他已经完成了项目的搭建和gpt模型的调试。接下来要改成百度千帆的模型,却遇到了难题。其实很简单,根据项目的框架走就可以了。正常部署环境过后(再次会遇到依赖安装不上,版本不匹配等诸多问题,按照报错排错修改即可)。根据readme生成数据模型之后。接下来就该调试ask_llm.py这一步开始了正式的模型修改了。
首先更改一下init方式
# 初始化百度千帆的api
init_qianfan(args.QIANFAN_ACCESS_KEY, args.QIANFAN_SECRET_KEY, args.model)然后查看到init方法是自己写的chatgpt的接口解析,我们就需要模仿人家的写法写一个百度千帆的,根据ERNIE_Speed_128K接口模型进行调试更改
https://cloud.baidu.com/doc/WENXINWORKSHOP/s/6ltgkzya5
之后得出了如下的脚本qianfan.py
import json.decoder
import qianfan
import os
from utils.enums import LLM
import time
def init_qianfan(QIANFAN_ACCESS_KEY, QIANFAN_SECRET_KEY,model):
os.environ["QIANFAN_ACCESS_KEY"] = QIANFAN_ACCESS_KEY
os.environ["QIANFAN_SECRET_KEY"] = QIANFAN_SECRET_KEY
# def init_qianfan(QIANFAN_ACCESS_KEY, QIANFAN_SECRET_KEY, model):
# qianfan.AccessKey(QIANFAN_ACCESS_KEY)
# qianfan.SecretKey(QIANFAN_SECRET_KEY)
# os.environ["QIANFAN_ACCESS_KEY"] = QIANFAN_ACCESS_KEY
# os.environ["QIANFAN_SECRET_KEY"] = QIANFAN_SECRET_KEY
# 处理单轮对话的completion任务
def ask_completion(model, batch, temperature):
completion = qianfan.Completion()
response = completion.do(
model=model,
prompt=batch, # 这是当前问题
temperature=temperature,
max_output_tokens=200, # 最大输出token数量,根据需要调整
top_p=1,
frequency_penalty=0,
presence_penalty=0,
stop=[";"]
)
# 提取response中的结果部分
response_clean = [response["result"]]
return dict(
response=response_clean,
prompt_tokens=response["usage"]["prompt_tokens"],
completion_tokens=response["usage"]["completion_tokens"],
total_tokens=response["usage"]["total_tokens"]
)
# 处理多轮对话的任务
def ask_chat(model, messages: list, temperature, n):
chat_completion = qianfan.ChatCompletion()
response = chat_completion.do(
model=model,
messages=messages, # messages 是带有历史对话的消息列表
temperature=temperature,
max_output_tokens=200 # 最大输出token数量,根据需要调整
)
# 提取返回的消息内容
response_clean = [response["result"]]
if n == 1:
response_clean = response_clean[0]
return dict(
response=response_clean,
prompt_tokens=response["usage"]["prompt_tokens"],
completion_tokens=response["usage"]["completion_tokens"],
total_tokens=response["usage"]["total_tokens"]
)
# 调用对话请i去函数,p判断ask_completion/ask_chat
def ask_llm(model: str, batch: list, temperature: float, n: int):
n_repeat = 0
while True:
try:
if model in LLM.TASK_COMPLETIONS: # completion任务
assert n == 1
response = ask_completion(model, batch, temperature)
elif model in LLM.TASK_CHAT: # chat任务
assert len(batch) == 1, "batch must be 1 in this mode"
messages = [{"role": "user", "content": batch[0]}]
response = ask_chat(model, messages, temperature, n)
response['response'] = [response['response']]
break
except json.decoder.JSONDecodeError:
n_repeat += 1
print(f"Repeat for the {n_repeat} times for JSONDecodeError", end="\n")
time.sleep(1)
continue
except Exception as e:
n_repeat += 1
print(f"Repeat for the {n_repeat} times for exception: {e}", end="\n")
time.sleep(1)
continue
return response接下来你如果运行会发现在ask_llm的时候异常会报错,这是因为异常不匹配,我没有细察qianfan的异常有那些,就直接抛出Exception
try:
res = ask_llm(args.model, batch, args.temperature, args.n)
except Exception as e:
print(f"The {i}-th question has too much tokens! Return \"SELECT\" instead")
# res = ""
res = {"response": [""], "total_tokens": 0}因为二者模型不一样,还需要对结果集进行数据的搜集更改,我这里没做处理,其实只需要一个简单的正则表达式就可以,在如下更改就可以了。
for sqls, db_id in zip(res["response"], cur_db_ids):
processed_sqls = []
for sql in sqls:
sql = " ".join(sql.replace("\n", " ").split())
sql = process_duplication(sql)
if sql.startswith("SELECT"):
pass
elif sql.startswith(" "):
sql = "SELECT" + sql
else:
sql = "SELECT " + sql
processed_sqls.append(sql)由于我没做更改,只得在后续生成的文件中进行数据提取,采用如下方法
def extract_sql(content):
# 匹配```sql开头 ```结尾
pattern = r'```sql(.*?)```'
sql_blocks = re.findall(pattern, content, re.DOTALL)
sql_statements = []
for sql in sql_blocks:
cleaned_sql = " ".join(sql.split())
sql_statements.append(cleaned_sql)
return sql_statements同时还需要再enmus脚本中添加对应的模型来识别
class LLM:
# openai LLMs
TEXT_DAVINCI_003 = "text-davinci-003"
CODE_DAVINCI_002 = "code-davinci-002"
GPT_35_TURBO = "gpt-3.5-turbo"
GPT_35_TURBO_0613 = "gpt-3.5-turbo-0613"
GPT_35_TURBO_16K = "gpt-3.5-turbo-16k"
GPT_35_TURBO_0301 = "gpt-3.5-turbo-0301"
GPT_4 = "gpt-4"
ERNIE_Speed_128K = 'ERNIE-Speed-128K'
# LLMs that use openai completion api
TASK_COMPLETIONS = [
TEXT_DAVINCI_003,
CODE_DAVINCI_002
]
# LLMs that use openai chat api
TASK_CHAT = [
GPT_35_TURBO,
GPT_35_TURBO_0613,
GPT_35_TURBO_16K,
GPT_35_TURBO_0301,
GPT_4,
ERNIE_Speed_128K
]脚本ask_llm输入的命令行修改为类似如下的方式
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument("--question", type=str)
parser.add_argument("--QIANFAN_ACCESS_KEY", type=str)
parser.add_argument("--QIANFAN_SECRET_KEY", type=str)
# parser.add_argument("--openai_api_key", type=str)
# parser.add_argument("--openai_group_id", type=str, default="org-ktBefi7n9aK7sZjwc2R9G1Wo")
parser.add_argument("--model", type=str, choices=[LLM.TEXT_DAVINCI_003,
LLM.GPT_35_TURBO,
LLM.GPT_35_TURBO_0613,
# LLM.TONG_YI_QIAN_WEN,
LLM.GPT_35_TURBO_16K,
LLM.GPT_4,
LLM.ERNIE_Speed_128K],
default=LLM.ERNIE_Speed_128K)
parser.add_argument("--start_index", type=int, default=0)
parser.add_argument("--end_index", type=int, default=1000000)
parser.add_argument("--temperature", type=float, default=0) # qianfan (0, 1.0]
parser.add_argument("--mini_index_path", type=str, default="")
parser.add_argument("--batch_size", type=int, default=1)
parser.add_argument("--n", type=int, default=5, help="Size of self-consistent set")
parser.add_argument("--db_dir", type=str, default="dataset/spider/database")注意千帆的temperature是 (0, 1.0]和gpt的还不一样
至此已经完全修改完毕。
]]>[
{
"id": "A",
"name": "农、林、牧、渔业",
"pid": null,
"level": "0",
"desc": "本门类包括 01~05 大类"
},
{
"id": "A01",
"name": "农业",
"pid": "A",
"level": "1",
"desc": "指对各种农作物的种植"
},
{
"id": "A011",
"name": "谷物种植",
"pid": "A01",
"level": "2",
"desc": "指以收获籽实为主的农作物的种植,包括稻 谷、小麦、玉米等农作物的种植和作为饲料和工业原料的谷物的种植"
},
{
"id": "A0111",
"name": "稻谷种植",
"pid": "A011",
"level": "3",
"desc": null
},
{
"id": "A0112",
"name": "小麦种植",
"pid": "A011",
"level": "3",
"desc": null
},
{
"id": "A0113",
"name": "玉米种植",
"pid": "A011",
"level": "3",
"desc": null
},
{
"id": "A0119",
"name": "其他谷物种植",
"pid": "A011",
"level": "3",
"desc": null
},
{
"id": "A012",
"name": "豆类、油料和薯类种植",
"pid": "A01",
"level": "2",
"desc": null
}
]然后将他们转换成这种形式
[
{
"id": "A",
"name": "农、林、牧、渔业",
"pid": null,
"level": "0",
"desc": "本门类包括 01~05 大类",
"children": [
{
"id": "A01",
"name": "农业",
"pid": "A",
"level": "1",
"desc": "指对各种农作物的种植",
"children": [
{
"id": "A011",
"name": "谷物种植",
"pid": "A01",
"level": "2",
"desc": "指以收获籽实为主的农作物的种植,包括稻 谷、小麦、玉米等农作物的种植和作为饲料和工业原料的谷物的种植",
"children": [
{
"id": "A0111",
"name": "稻谷种植",
"pid": "A011",
"level": "3",
"desc": null
},
{
"id": "A0112",
"name": "小麦种植",
"pid": "A011",
"level": "3",
"desc": null
}下面是python代码
# 划分同一个数据下面的各种类别
import json
# 读取文件并解析 JSON 数据
def read_json_file(file_path):
with open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:
data = json.load(file)
return data
# 写入到 JSON 文件
def write_json_file(data, file_path):
with open(file_path, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as file:
json.dump(data, file, ensure_ascii=False, indent=4)
def build_hierarchy(categories):
# 创建一个空的字典列表,用于存储最终结果
result = []
# 创建字典,用于将分类按照 id 分组
category_map = {}
for category in categories:
category_map[category['id']] = category
# 遍历分类列表,构建分类树
for category in categories:
# 如果当前分类的 pid 为空,则将其视为一级分类
if category['pid'] is None:
result.append(category)
# 否则,将当前分类添加到其父分类的 children 列表中
else:
parent_id = category['pid']
parent_category = category_map.get(parent_id)
if parent_category is not None:
if 'children' not in parent_category:
parent_category['children'] = []
parent_category['children'].append(category)
return result
# 读取数据
categories = read_json_file('D:\ALL_Proj\PyCharm_Proj\pythonProjectDemo01\无标题.json')
# 构建分类树
result = build_hierarchy(categories)
# 写入数据
write_json_file(result, 'D:\ALL_Proj\PyCharm_Proj\pythonProjectDemo01\Aresult.json')
print("文件写入成功")