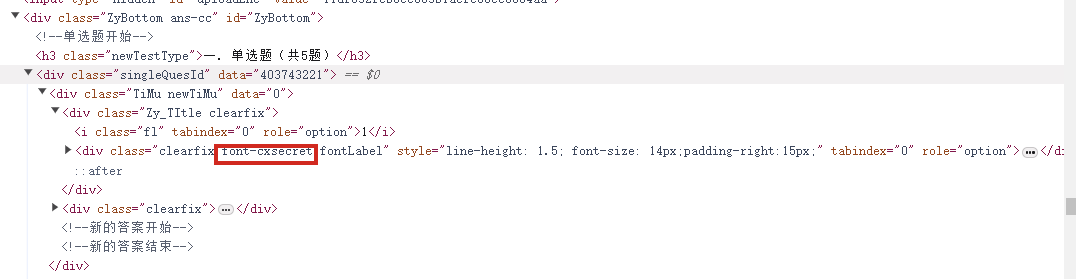
搜索页面和这个相关的从而定位到引入文件
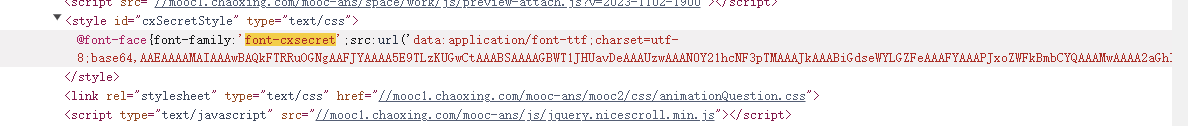
查找,一眼Base64编码的字体文件,通过这个编码数据解码获得原字体文件
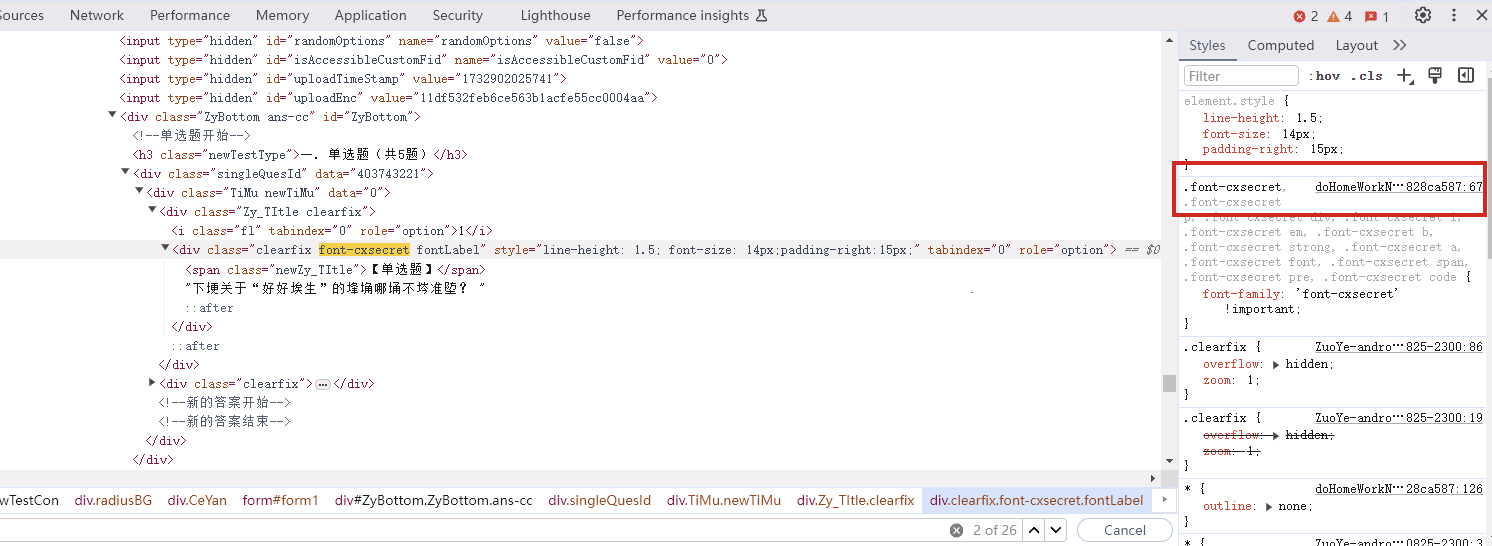
找到之后进去查看
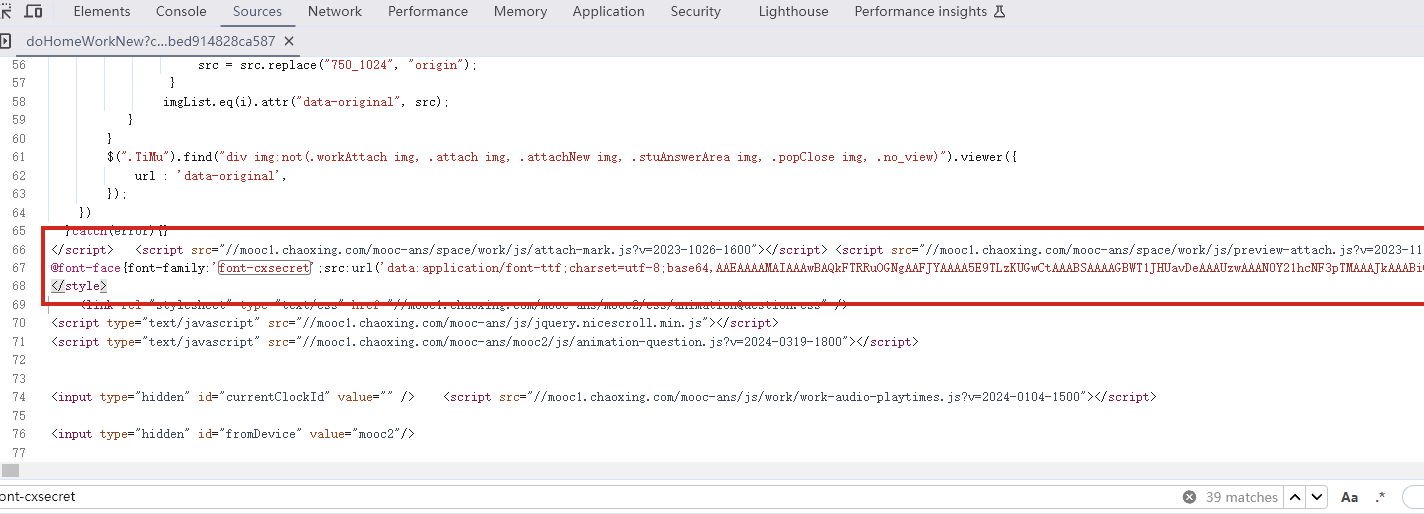
找到了,把里面内容复制下来,掐头去尾,是这样的数据
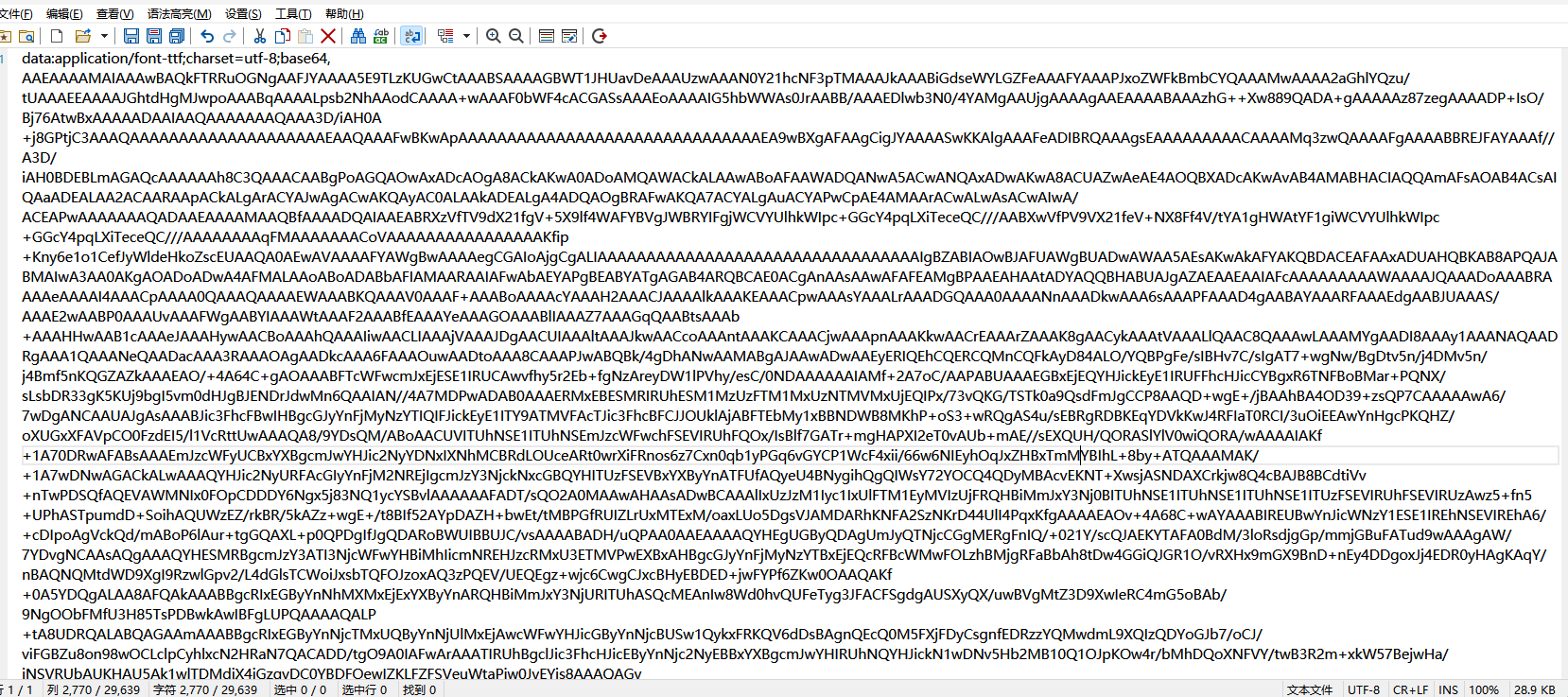
编写脚本进行解码,引号内填写base64编码数据去掉data:application/font-ttf;charset=utf-8;base64,的开头声明"
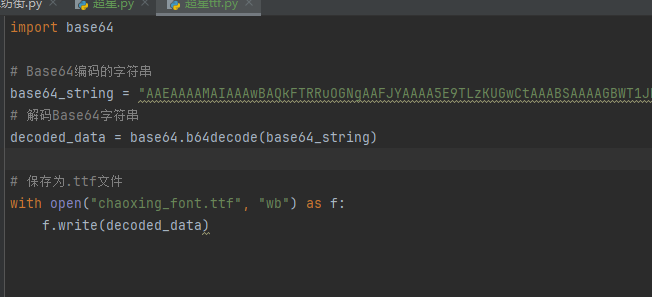
import base64
# Base64编码的字符串
base64_string = "这里填写base64编码数据去掉data:application/font-ttf;charset=utf-8;base64,的开头声明"
# 解码Base64字符串
decoded_data = base64.b64decode(base64_string)
# 保存为.ttf文件
with open("chaoxing_font.ttf", "wb") as f:
f.write(decoded_data)获得到base64的ttf文件结果
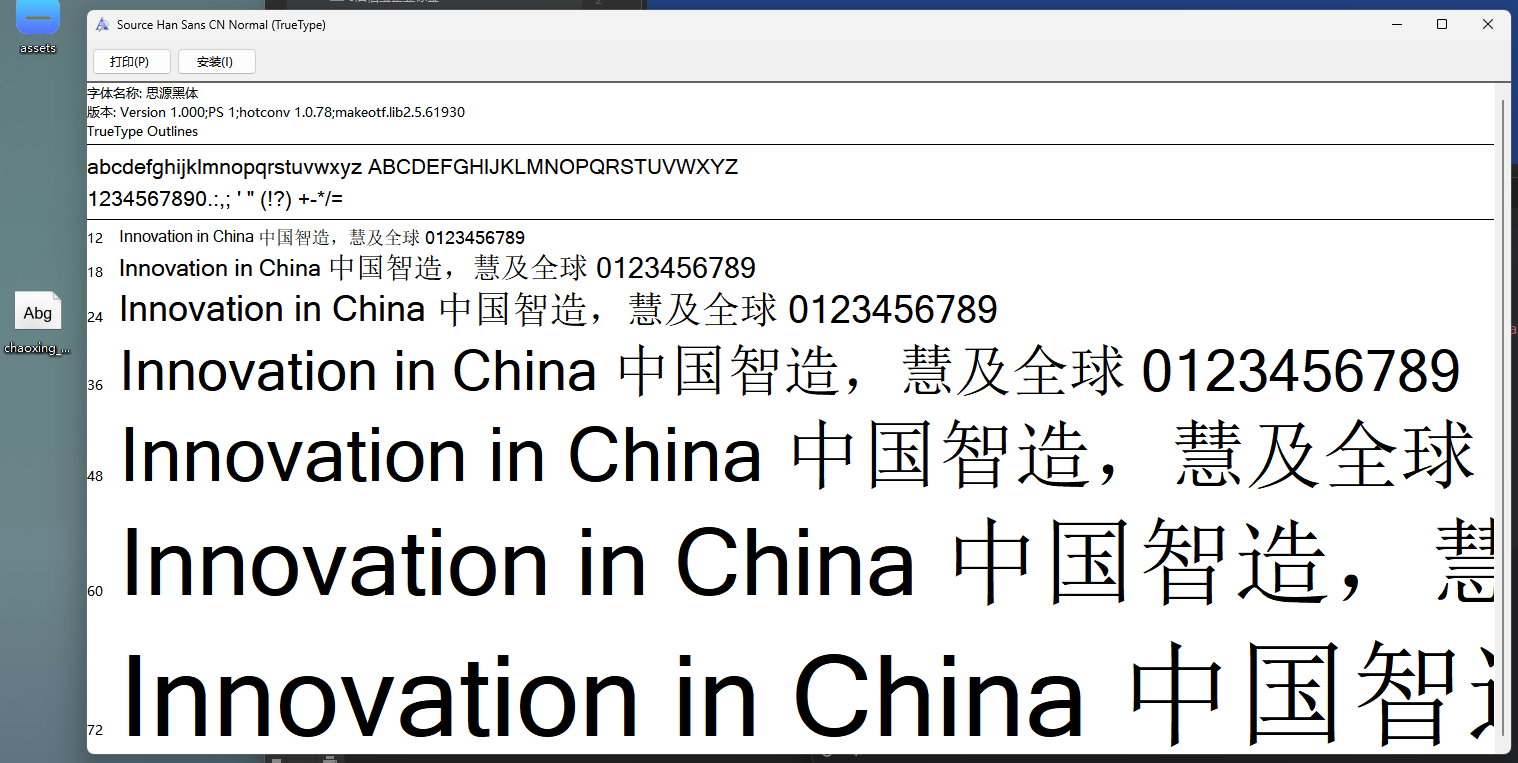
使用字体查看器查看字体 https://www.bejson.com/ui/font/
接下来将ttf文件转换成xml文件(python需要安装fontTools)
from fontTools.ttLib import TTFont
# TTF 文件路径
ttf_path = r"D:\UserData\Desktop\chaoxing_font.ttf"
xml_output_path = r"D:\UserData\Desktop\chaoxing_font.xml"
# 加载字体文件
font = TTFont(ttf_path)
# 保存为 XML 文件
font.saveXML(xml_output_path)
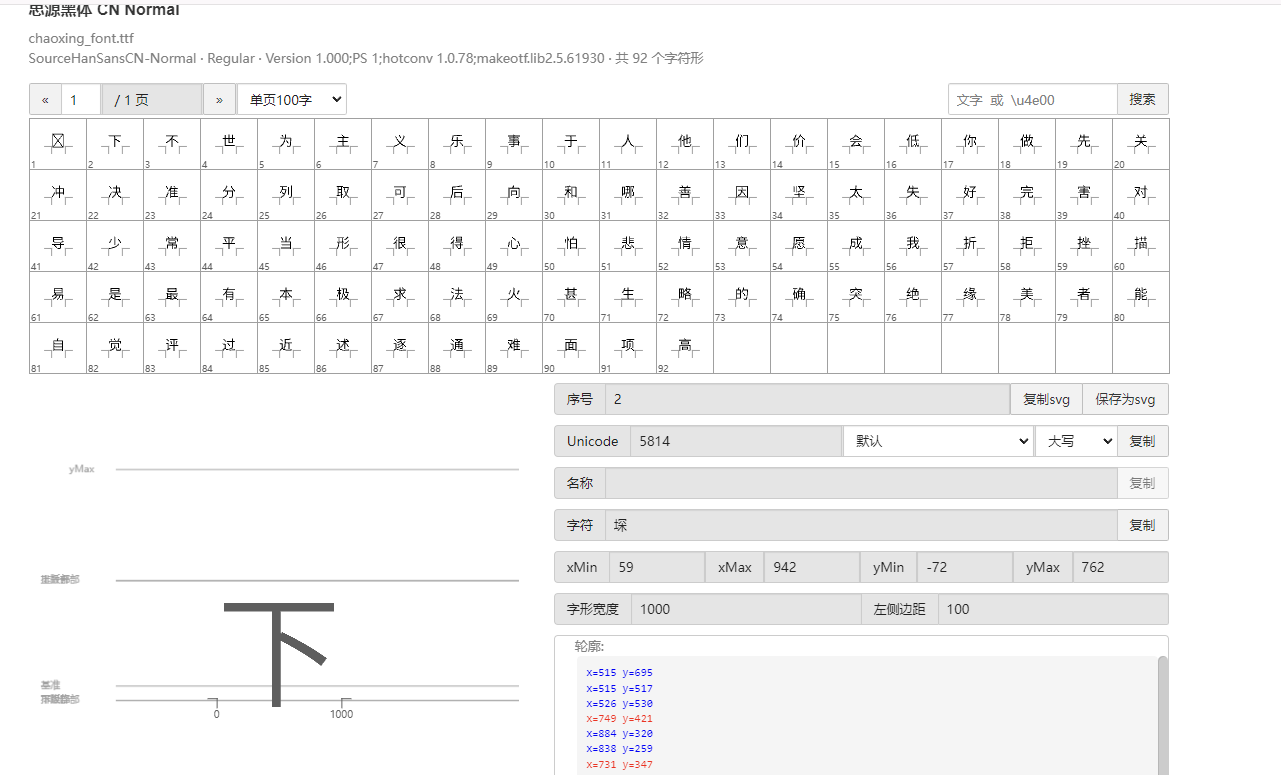
print(f"解析完毕")抽选字体对比一下映射结果对不对(超星的加密是修改了此字体图元数据,显示成未加密的字)
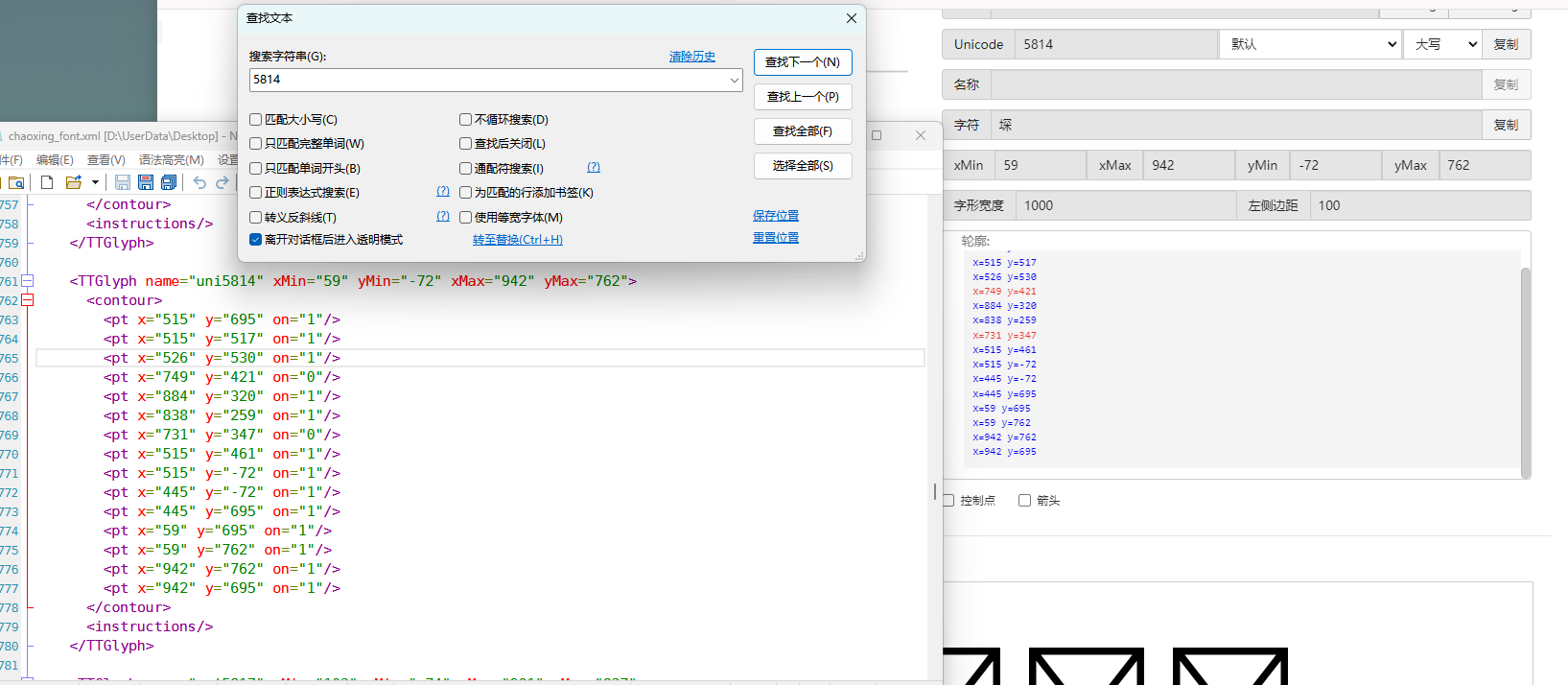
下载原来的字体文件(非超星加密后的文件)
源字体文件对应
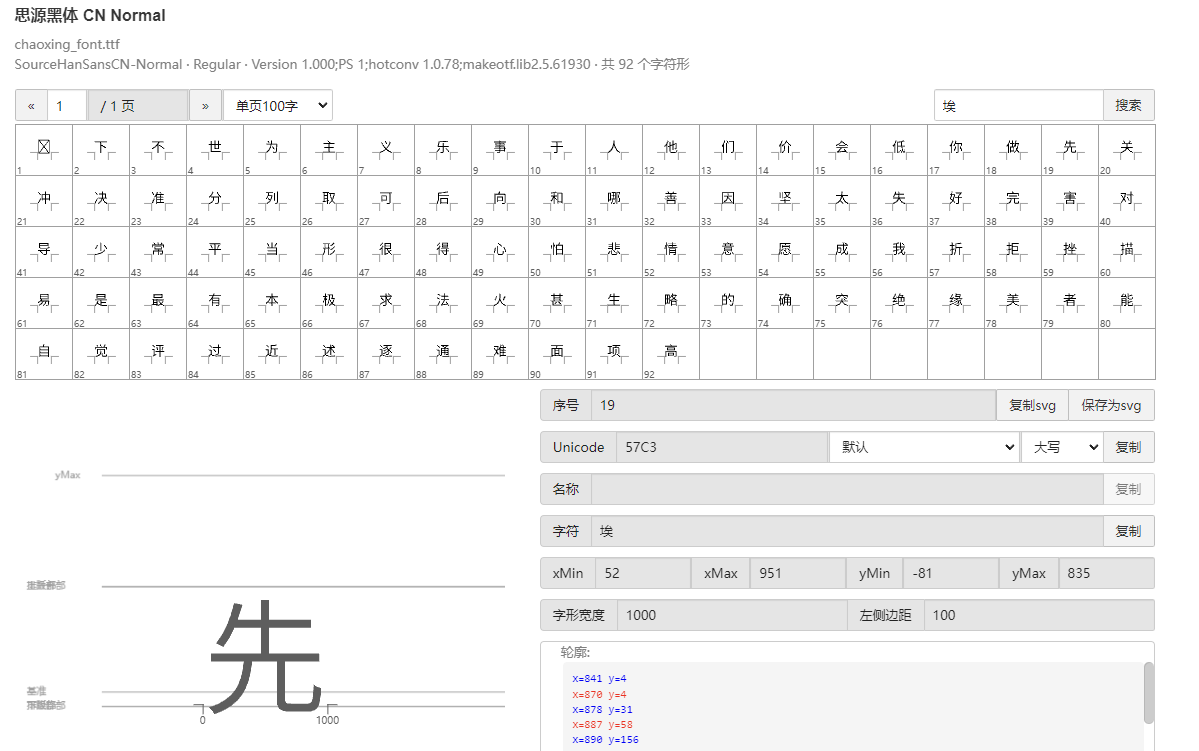
超星加密后字体
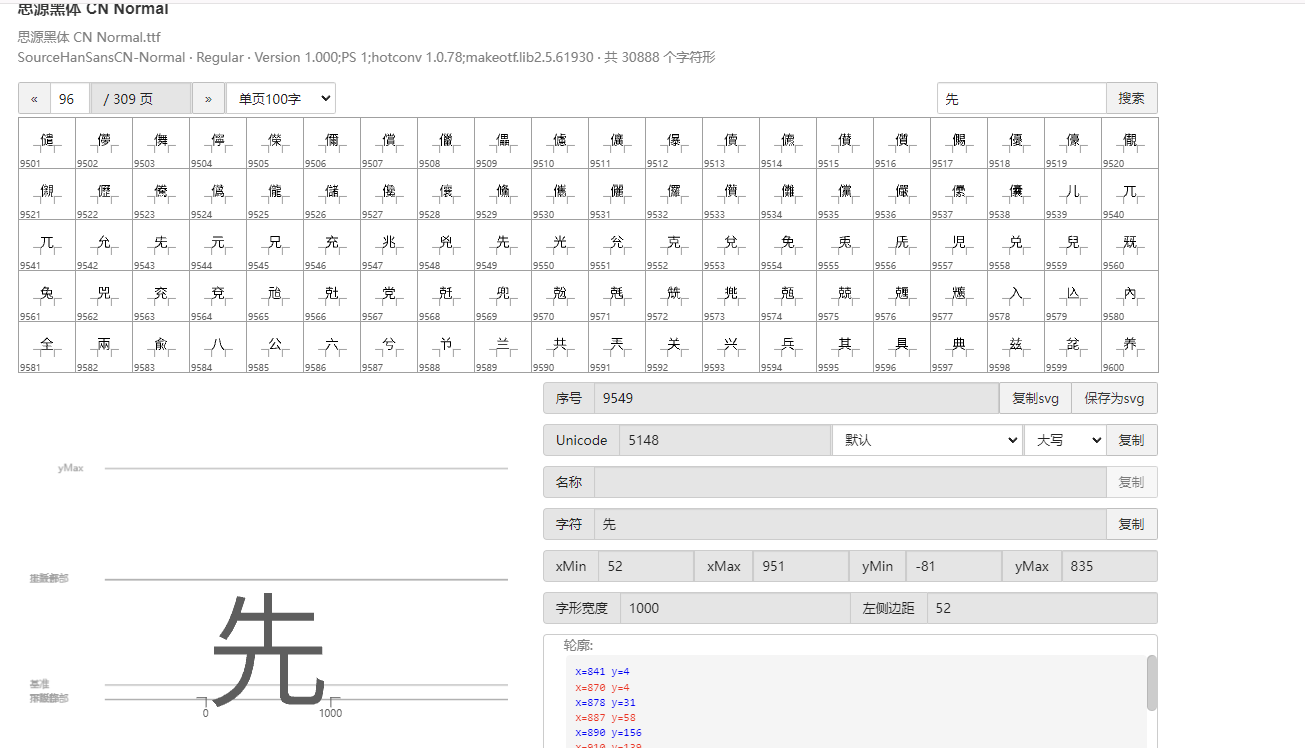
也就是说原来的5148对应着57C3
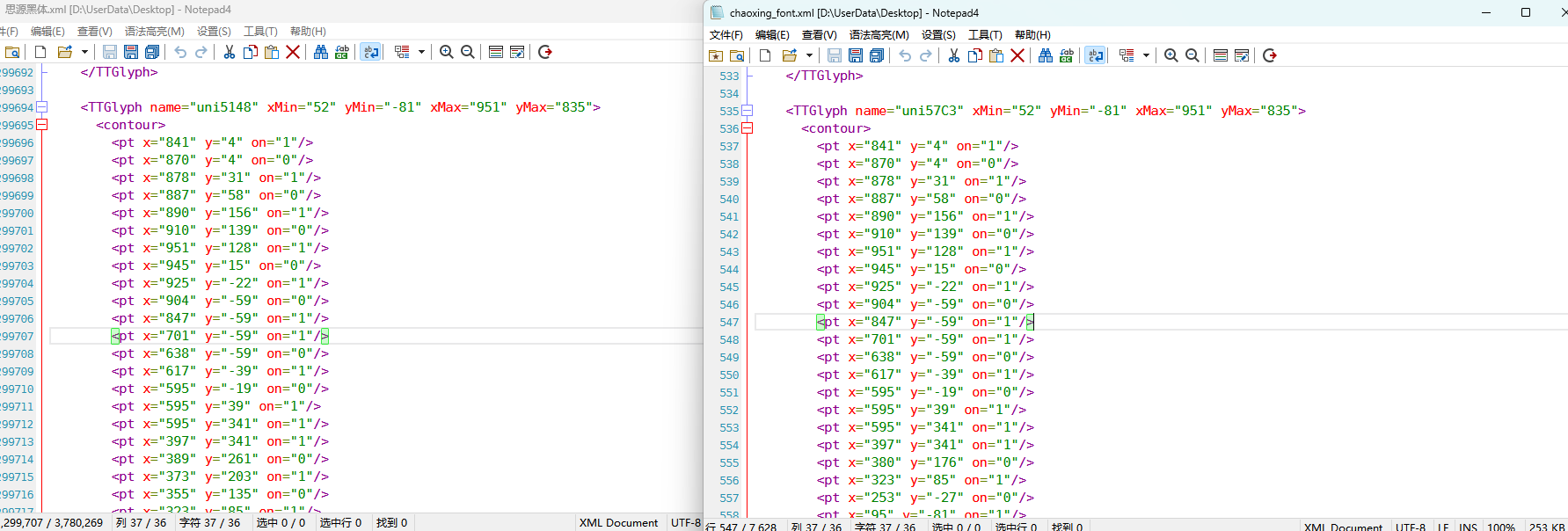
编写对比代码进行测试
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import hashlib
import json
def parse_glyphs(file_path):
"""
解析字体文件中的 TTGlyph 信息
"""
tree = ET.parse(file_path)
root = tree.getroot()
glyphs = {}
for glyph in root.findall(".//TTGlyph"):
name = glyph.get("name")
points = []
for pt in glyph.findall(".//pt"):
x = pt.get("x")
y = pt.get("y")
on = pt.get("on")
points.append(f"{x}{y}{on}")
# 生成轮廓的唯一哈希值
hash_value = hashlib.md5("".join(points).encode('utf-8')).hexdigest()
# 截取哈希值的 25-32 位来作为唯一标识
truncated_hash = hash_value[24:32]
glyphs[truncated_hash] = name # 使用截取后的哈希值作为键
return glyphs
def get_unicode_character(name):
"""
根据 glyph 名称(如 uni5148)获取对应汉字
"""
if name.startswith("uni"):
try:
unicode_value = int(name[3:], 16)
return chr(unicode_value)
except ValueError:
return None
return None
def build_mapping(xml_old_path, xml_cx_path):
"""
建立思源黑体和超星字体的对照关系
"""
old_glyphs = parse_glyphs(xml_old_path)
print(len(old_glyphs))
cx_glyphs = parse_glyphs(xml_cx_path)
print(len(cx_glyphs))
mapping = []
for cx_hash, cx_name in cx_glyphs.items():
if cx_hash in old_glyphs:
old_name = old_glyphs[cx_hash]
character = get_unicode_character(old_name)
if character: # 确保是有效汉字
mapping.append({
"chaoxing": cx_name,
"si_yuan": {
"siyuan_name": old_name,
"siyuan_name_value": character
}
})
return mapping
if __name__ == "__main__":
xml_old_path = r"D:\UserData\Desktop\思源黑体.xml"
xml_cx_path = r"D:\UserData\Desktop\chaoxing_font.xml"
result = build_mapping(xml_old_path, xml_cx_path)
# 输出到文件
with open("glyph_mapping.json", "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
json.dump(result, f, ensure_ascii=False, indent=4)
# 打印部分结果
# print(json.dumps(result[:5], ensure_ascii=False, indent=4))生成结果
[
{
"chaoxing": "uni57C2",
"si_yuan": {
"siyuan_name": "uni2FAF",
"siyuan_name_value": "⾯"
}
},
{
"chaoxing": "uni57E0",
"si_yuan": {
"siyuan_name": "uni5584",
"siyuan_name_value": "善"
}
},
{
"chaoxing": "uni580F",
"si_yuan": {
"siyuan_name": "uni4E16",
"siyuan_name_value": "世"
}
},
{
"chaoxing": "uni581D",
"si_yuan": {
"siyuan_name": "uni5BB3",
"siyuan_name_value": "害"
}
},
{
"chaoxing": "uni900B",
"si_yuan": {
"siyuan_name": "uni2F83",
"siyuan_name_value": "⾃"
}
}
]我采用的字符串是
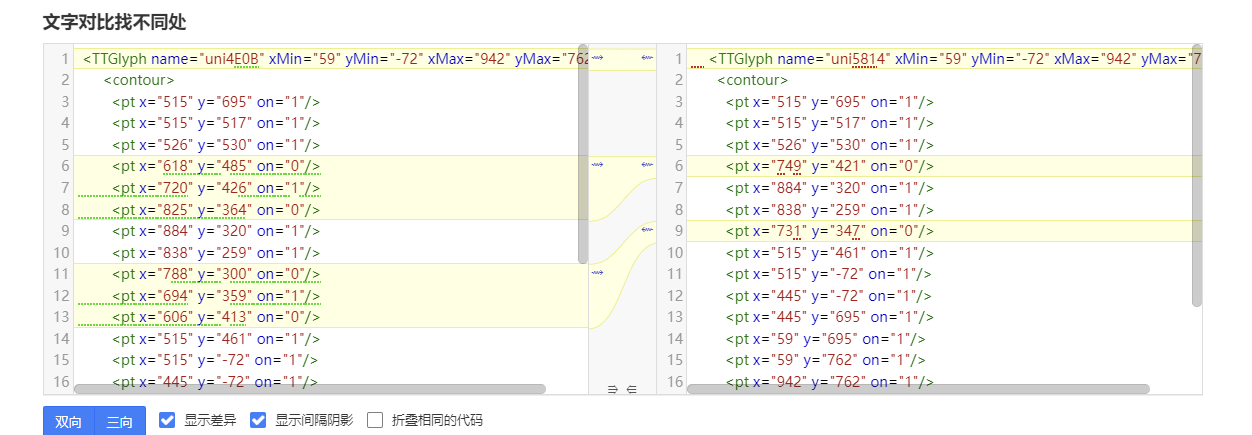
超星:下埂关于“好好埃生”的埄埆哪埇不埁准埅?
思源:下面关于“好好先生”的描述哪项不太准确?
结合对照表显示,发现字体字形数据并对不上,查看字体数据,针对“下“字进行分析,发现两边结果并对不上,结果是超星对于字体字形进行了更改,并不是简单的对比字符哈希值就可以对比出来的了。

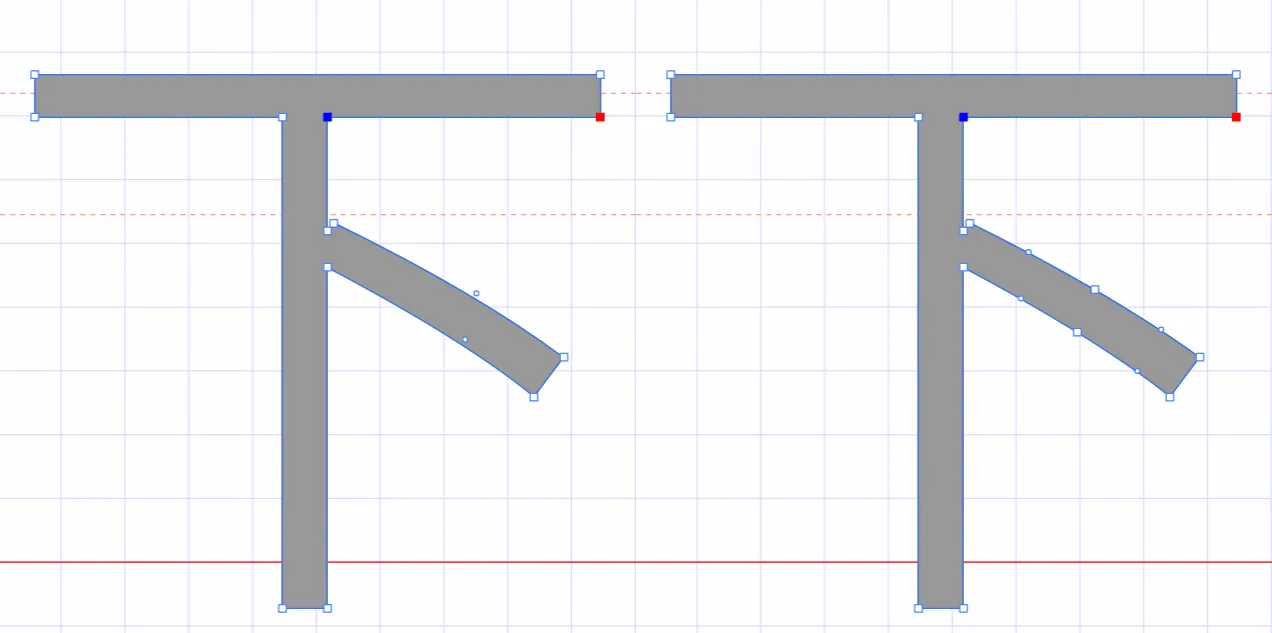
查看对比效果
左侧为原版字体,右侧为学习通字体
百度到” I Am I“大佬的文章”从学习通复制文字乱码看前端版权保护“找到一定的思路是假设字符的边距是唯一的,好的,那么我们就拼接边距距离。得出以下代码
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import hashlib
import json
def parse_glyphs(file_path):
"""
解析字体文件中的 TTGlyph 信息,使用 xMin, yMin, xMax, yMax 作为唯一标识
"""
tree = ET.parse(file_path)
root = tree.getroot()
glyphs = {}
for glyph in root.findall(".//TTGlyph"):
name = glyph.get("name")
# 获取 xMin, yMin, xMax, yMax
xMin = glyph.get("xMin")
yMin = glyph.get("yMin")
xMax = glyph.get("xMax")
yMax = glyph.get("yMax")
# 使用这四个值拼接成唯一标识符
if xMin and yMin and xMax and yMax:
unique_key = f"{xMin}{yMin}{xMax}{yMax}"
glyphs[unique_key] = name # 用四个边界值作为唯一键,值为glyph名称
return glyphs
# def parse_glyphs(file_path):
# """
# 解析字体文件中的 TTGlyph 信息
# """
# tree = ET.parse(file_path)
# root = tree.getroot()
#
# glyphs = {}
#
# for glyph in root.findall(".//TTGlyph"):
# name = glyph.get("name")
# points = []
# for pt in glyph.findall(".//pt"):
# x = pt.get("x")
# y = pt.get("y")
# on = pt.get("on")
# points.append(f"{x}{y}{on}")
#
# # 生成轮廓的唯一哈希值
# hash_value = hashlib.md5("".join(points).encode('utf-8')).hexdigest()
# glyphs[hash_value] = name # 哈希值对应 glyph 名称
#
# return glyphs
def get_unicode_character(name):
"""
根据 glyph 名称(如 uni5148)获取对应汉字
"""
if name.startswith("uni"):
try:
unicode_value = int(name[3:], 16)
return chr(unicode_value)
except ValueError:
return None
return None
def build_mapping(xml_old_path, xml_cx_path):
"""
建立思源黑体和超星字体的对照关系
"""
old_glyphs = parse_glyphs(xml_old_path)
# print(len(old_glyphs))
cx_glyphs = parse_glyphs(xml_cx_path)
# print(len(cx_glyphs))
# print(cx_glyphs)
mapping = []
for cx_hash, cx_name in cx_glyphs.items():
if cx_hash in old_glyphs:
old_name = old_glyphs[cx_hash]
character = get_unicode_character(old_name)
if cx_name == 'uni5814':
print(cx_hash)
print(old_name)
if character: # 确保是有效汉字
mapping.append({
"chaoxing": cx_name,
"si_yuan" : {
"siyuan_name": old_name,
"siyuan_name_value": character
}
})
return mapping
if __name__ == "__main__":
xml_old_path = r"D:\UserData\Desktop\思源黑体.xml"
xml_cx_path = r"D:\UserData\Desktop\chaoxing_font.xml"
result = build_mapping(xml_old_path, xml_cx_path)
# 输出到文件
with open("glyph_mapping.json", "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
json.dump(result, f, ensure_ascii=False, indent=4)
# 打印部分结果
# print(json.dumps(result[:5], ensure_ascii=False, indent=4))再通过匹配结果进行查看数据
import json
# 读取json
def load_mapping(file_path):
with open(file_path, "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
return json.load(f)
# 获取字符对应的 uni 名称
def get_uni_name(character, mapping):
unicode_name = f"uni{ord(character):X}"
# print(unicode_name)
for entry in mapping:
if entry["chaoxing"] == unicode_name:
return entry
return None
# 解析字符串
def parse_code(code, mapping):
result = []
for char in code:
mapping_entry = get_uni_name(char, mapping)
if mapping_entry:
result.append({
"char": char,
"message": mapping_entry["si_yuan"]['siyuan_name_value']
})
else:
result.append({
"char": char,
"message": char
})
return result
# 测试代码
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 读取字形映射
glyph_mapping_file = "glyph_mapping.json"
mapping = load_mapping(glyph_mapping_file)
# 示例字符串
code = '下埂关于“好好埃生”的埄埆哪埇不埁准埅?'
# 解析字符串
parsed_result = parse_code(code, mapping)
# 输出解析结果
# for item in parsed_result:
# print(item)
print(f'超星字体:{code}')
siyuan_font = ''.join([item['message'] for item in parsed_result])
print(f'思源字体:{siyuan_font}')得出结果
超星字体:下埂关于“好好埃生”的埄埆哪埇不埁准埅?
思源字体:下⾯关于“好好先生”的描述哪项不太准确?在大佬的测试中,是可以确定90%左右的字符数据的。如果您不想看了,到这里就可以了,基本满足所有的效果了。
然后由于最近领导给我一些任务就是比较两个字符串的相似度,通过这个启发就想通过xy向量计算字符字形的相似度。得出以下代码,首先针对”下”字进行数据测试
归一化:将所有点归一化到相同的尺度。(如果不归一,DTW有要求长度一样,会报错)
归一化点集(Normalization of points)是指将原始点集中的每个点的坐标变换到一个特定的标准范围,以消除由于坐标范围不同而引起的差异,从而使得数据的比较更加公正和一致。具体而言,在这段代码中,归一化的目标是将每个点的坐标缩放到
[0, 1]的范围内。为什么要进行归一化?
在计算点集之间的相似度时(如使用动态时间规整 DTW),不同的点集可能有不同的坐标范围或单位。如果不进行归一化,可能会因为坐标差异较大,导致计算出的相似度偏差较大。归一化的过程能够消除这种影响,让两个点集具有相同的尺度,从而公平地比较它们之间的相似性。
举个例子:
假设有一个点集:
points = [(10, 20), (30, 40), (50, 60), (70, 80)]经过归一化处理后:
- 最小值:
min_x = 10,min_y = 20 - 最大值:
max_x = 70,max_y = 80
每个点将会变成:
(10, 20)变成(0, 0)(30, 40)变成(0.333, 0.333)(50, 60)变成(0.666, 0.666)(70, 80)变成(1, 1)
最终,这些点就会被归一化到
[0, 1]的范围内,这样它们的尺度是一致的,适合用于后续的相似度计算。归一化的目的是消除不同点集之间的坐标尺度差异,使得不同的点集可以在相同的尺度下进行比较。通过这种方式,我们可以更加公平地计算它们之间的相似度,而不会因为坐标的差异导致错误的比较结果。- 最小值:
使用DTW进行点对齐:保持原有的DTW对齐方法。
这里计算两个点集的相似度分数,通过DTW距离计算得出一个0~1的相似度分数。1完全相似,0完全不一样。
函数使用
fastdtw函数计算归一化后的两个点集之间的 DTW 距离。DTW 是一种衡量两组时间序列相似度的算法,常用于处理不等长、速度不同的序列数据。在这里,它也可以用于比较两个二维点集的相似度。- 计算相似度:基于对齐后的点集计算相似度。
import numpy as np
from fastdtw import fastdtw
from scipy.spatial.distance import euclidean
# 假设我们已经有了两个字形的数据
ttglyph_superstar = [
(515, 695), (515, 517), (526, 530), (749, 421), (884, 320),
(838, 259), (731, 347), (515, 461), (515, -72), (445, -72),
(445, 695), (59, 695), (59, 762), (942, 762), (942, 695)
]
ttglyph_sourcehan = [
(515, 695), (515, 517), (526, 530), (618, 485), (720, 426),
(825, 364), (884, 320), (838, 259), (788, 300), (694, 359),
(606, 413), (515, 461), (515, -72), (445, -72), (445, 695),
(59, 695), (59, 762), (942, 762), (942, 695)
]
# 转换为numpy数组
points1 = np.array(ttglyph_superstar)
points2 = np.array(ttglyph_sourcehan)
def normalize_points(points):
"""
归一化点集
"""
if len(points) == 0: # 检查点集是否为空
return []
points = np.array(points) # 将点集转换为NumPy数组
min_x, min_y = np.min(points, axis=0)
max_x, max_y = np.max(points, axis=0)
# 防止除以零
if max_x == min_x:
max_x = min_x + 1
if max_y == min_y:
max_y = min_y + 1
normalized_points = (points - [min_x, min_y]) / [max_x - min_x, max_y - min_y]
return normalized_points
def calculate_similarity(points1, points2):
"""
使用DTW计算两个点集之间的相似度
"""
points1_normalized = normalize_points(points1)
points2_normalized = normalize_points(points2)
if len(points1_normalized) == 0 or len(points2_normalized) == 0:
return 0.0 # 如果任一点集为空,相似度为0
#distance 是 DTW 算法计算出来的总距离,表示两个点集的整体差异。
#path 是 DTW 算法找到的最佳对齐路径,指示了如何从 points1 映射到 points2。
distance, path = fastdtw(points1_normalized, points2_normalized, dist=euclidean)
# DTW 算法会计算出一组“对齐”路径,通过这个路径可以重新排列两个点集,使它们更好地对齐。根据 path 的内容,分别从 points1_normalized 和 points2_normalized 中提取对齐后的点集。
aligned_points1 = [points1_normalized[i] for i, _ in path]
aligned_points2 = [points2_normalized[j] for _, j in path]
# 计算对齐点之间的欧几里得距离,在最佳对齐下,每对点之间的差异。np.linalg.norm 计算的是两点之间的欧几里得距离
distances = [np.linalg.norm(np.array(p1) - np.array(p2)) for p1, p2 in zip(aligned_points1, aligned_points2)]
# 算出所有欧氏距离去平局书,得出平均欧氏距距离
average_distance = np.mean(distances)
similarity_score = 1 / (1 + average_distance)
return similarity_score
print(f"Similarity score: {calculate_similarity(points2,points1)}")得出结果
Similarity score: 0.975700703557036发现相似度还是很高的,这里是需要忽略字体的风格的,和笔画的这些。
好的,可以通过这种相似度算法去核对超星字体对应的元数据了。
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import json
import numpy as np
from fastdtw import fastdtw
from scipy.spatial.distance import euclidean
from tqdm import tqdm
def parse_glyphs(file_path):
"""
解析字体文件中的 TTGlyph 信息
"""
tree = ET.parse(file_path)
root = tree.getroot()
glyphs = {}
for glyph in root.findall(".//TTGlyph"):
name = glyph.get("name")
points = []
for pt in glyph.findall(".//pt"):
x = int(pt.get("x"))
y = int(pt.get("y"))
on = int(pt.get("on", 0)) # 默认值为0,如果不存在则设为0
points.append((x, y))
# 将点集转换为字符串,作为字典的键
key = str(points)
glyphs[key] = name
return glyphs
def get_unicode_character(name):
"""
根据 glyph 名称(如 uni5148)获取对应汉字
"""
if name.startswith("uni"):
try:
unicode_value = int(name[3:], 16)
return chr(unicode_value)
except ValueError:
return None
return None
def normalize_points(points):
"""
归一化点集
"""
if not points: # 检查点集是否为空
return []
points = np.array(points) # 将点集转换为NumPy数组
min_x, min_y = np.min(points, axis=0)
max_x, max_y = np.max(points, axis=0)
# 防止除以零
if max_x == min_x:
max_x = min_x + 1
if max_y == min_y:
max_y = min_y + 1
normalized_points = (points - [min_x, min_y]) / [max_x - min_x, max_y - min_y]
return normalized_points
def calculate_similarity(points1, points2):
"""
使用DTW计算两个点集之间的相似度
"""
points1_normalized = normalize_points(points1)
points2_normalized = normalize_points(points2)
if len(points1_normalized) == 0 or len(points2_normalized) == 0:
return 0.0 # 如果任一点集为空,相似度为0
distance, path = fastdtw(points1_normalized, points2_normalized, dist=euclidean)
aligned_points1 = [points1_normalized[i] for i, _ in path]
aligned_points2 = [points2_normalized[j] for _, j in path]
distances = [np.linalg.norm(np.array(p1) - np.array(p2)) for p1, p2 in zip(aligned_points1, aligned_points2)]
average_distance = np.mean(distances)
similarity_score = 1 / (1 + average_distance)
return similarity_score
def build_mapping(xml_old_path, xml_cx_path):
"""
建立思源黑体和超星字体的对照关系
"""
old_glyphs = parse_glyphs(xml_old_path)
print(f'思源字体:{len(old_glyphs)}')
cx_glyphs = parse_glyphs(xml_cx_path)
print(f'超星字体:{len(cx_glyphs)}')
mapping = []
total_combinations = len(old_glyphs) * len(cx_glyphs)
with tqdm(total=total_combinations, desc="Processing") as pbar:
for old_key, old_name in old_glyphs.items():
for cx_key, cx_name in cx_glyphs.items():
similarity = calculate_similarity(eval(old_key), eval(cx_key))
if similarity >= 0.9:
mapping.append({
"chaoxing": {
"cx_name": cx_name,
"cx_character": get_unicode_character(cx_name)
},
"si_yuan": {
"sy_name": old_name,
"sy_character": get_unicode_character(old_name)
},
"similarity": similarity
})
pbar.update(1)
return mapping
if __name__ == "__main__":
xml_old_path = r"D:\UserData\Desktop\思源黑体.xml"
xml_cx_path = r"D:\UserData\Desktop\chaoxing_font.xml"
result = build_mapping(xml_old_path, xml_cx_path)
# 输出到文件
with open("glyph_mapping2.json", "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
json.dump(result, f, ensure_ascii=False, indent=4)
# print(json.dumps(result[:5], ensure_ascii=False, indent=4))但是运行效果不如人意
这么长的时间肯定是不能忍的,所有采用多线程的处理方式,cpu就应该忙起来了。
from concurrent.futures import ProcessPoolExecutor, as_completed
import json
import numpy as np
from fastdtw import fastdtw
from scipy.spatial.distance import euclidean
from tqdm import tqdm
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
# 其他函数不变,保持之前的代码
def calculate_similarity(points1, points2):
"""
使用DTW计算两个点集之间的相似度
"""
points1_normalized = normalize_points(points1)
points2_normalized = normalize_points(points2)
if len(points1_normalized) == 0 or len(points2_normalized) == 0:
return 0.0 # 如果任一点集为空,相似度为0
distance, path = fastdtw(points1_normalized, points2_normalized, dist=euclidean)
aligned_points1 = [points1_normalized[i] for i, _ in path]
aligned_points2 = [points2_normalized[j] for _, j in path]
distances = [np.linalg.norm(np.array(p1) - np.array(p2)) for p1, p2 in zip(aligned_points1, aligned_points2)]
average_distance = np.mean(distances)
similarity_score = 1 / (1 + average_distance)
return similarity_score
def normalize_points(points):
"""
归一化点集
"""
if not points: # 检查点集是否为空
return []
points = np.array(points) # 将点集转换为NumPy数组
min_x, min_y = np.min(points, axis=0)
max_x, max_y = np.max(points, axis=0)
# 防止除以零
if max_x == min_x:
max_x = min_x + 1
if max_y == min_y:
max_y = min_y + 1
normalized_points = (points - [min_x, min_y]) / [max_x - min_x, max_y - min_y]
return normalized_points
def parallel_calculate_similarity(old_key, old_name, cx_glyphs):
"""
并行计算相似度
"""
results = []
for cx_key, cx_name in cx_glyphs.items():
similarity = calculate_similarity(eval(old_key), eval(cx_key))
if similarity >= 0.9:
results.append({
"chaoxing": {
"cx_name": cx_name,
"cx_character": get_unicode_character(cx_name)
},
"si_yuan": {
"sy_name": old_name,
"sy_character": get_unicode_character(old_name)
},
"similarity": similarity
})
return results
def get_unicode_character(name):
"""
根据 glyph 名称(如 uni5148)获取对应汉字
"""
if name.startswith("uni"):
try:
unicode_value = int(name[3:], 16)
return chr(unicode_value)
except ValueError:
return None
return None
def parse_glyphs(file_path):
"""
解析字体文件中的 TTGlyph 信息
"""
tree = ET.parse(file_path)
root = tree.getroot()
glyphs = {}
for glyph in root.findall(".//TTGlyph"):
name = glyph.get("name")
points = []
for pt in glyph.findall(".//pt"):
x = int(pt.get("x"))
y = int(pt.get("y"))
on = int(pt.get("on", 0)) # 默认值为0,如果不存在则设为0
points.append((x, y))
# 将点集转换为字符串,作为字典的键
key = str(points)
glyphs[key] = name
return glyphs
def build_mapping_parallel(xml_old_path, xml_cx_path):
"""
并行建立思源黑体和超星字体的对照关系
"""
old_glyphs = parse_glyphs(xml_old_path)
print(f'思源字体:{len(old_glyphs)}')
cx_glyphs = parse_glyphs(xml_cx_path)
print(f'超星字体:{len(cx_glyphs)}')
mapping = []
# 使用进程池进行并行处理
with ProcessPoolExecutor() as executor:
futures = []
# 为每个思源字体字形提交任务
for old_key, old_name in old_glyphs.items():
futures.append(executor.submit(parallel_calculate_similarity, old_key, old_name, cx_glyphs))
# 通过 as_completed 获取计算结果
for future in tqdm(as_completed(futures), total=len(futures), desc="Processing"):
mapping.extend(future.result())
return mapping
if __name__ == "__main__":
xml_old_path = r"D:\UserData\Desktop\思源黑体.xml"
xml_cx_path = r"D:\UserData\Desktop\chaoxing_font.xml"
result = build_mapping_parallel(xml_old_path, xml_cx_path)
# 输出到文件
with open("glyph_mapping_parallel.json", "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
json.dump(result, f, ensure_ascii=False, indent=4)
# 打印部分结果
print(json.dumps(result[:5], ensure_ascii=False, indent=4))这样处理时间来到了半小时(不过cpu要满了),因为我要求把大于0.9的数据全弄出来了,所以会有很多重复的字形数据。这里还需要取出相似度最高的那一个字形数据。
import json
# 读取保存的结果文件并生成包含所有相似度最高数据的 high.json 文件
def find_most_similar_for_all(result_file="glyph_mapping_parallel.json", output_file="high.json"):
# 读取 JSON 数据
with open(result_file, "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
data = json.load(f)
# 用于存储每个 chaoxing 对应的最相似的 si_yuan 对照项
highest_similarity_entries = {}
# 遍历所有条目,找出每个 chaoxing 字符对应的最相似的 si_yuan 对照项
for entry in data:
cx_name = entry["chaoxing"]["cx_name"]
similarity = entry["similarity"]
# 如果该 cx_name 没有出现过,或者当前相似度更高,更新最相似的条目
if cx_name not in highest_similarity_entries or similarity > highest_similarity_entries[cx_name]["similarity"]:
highest_similarity_entries[cx_name] = entry
# print(len(highest_similarity_entries))
# 将结果保存到 high.json 文件
with open(output_file, "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
json.dump(list(highest_similarity_entries.values()), f, ensure_ascii=False, indent=4)
print(f"已将结果保存到 {output_file}")
# 调用函数,生成 high.json 文件
find_most_similar_for_all()至此,我们以及彻底完成了映射表的制作。然后拿数据跑一下进行测试
import json
# 读取 high.json 文件并加载数据
def load_high_json(file_path="high.json"):
with open(file_path, "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
return json.load(f)
# 根据 high.json 匹配字符串中的每个字符,返回结果字符串
def match_string_with_high_json(code, high_json_data):
result = []
for char in code:
# 遍历 high.json 中的所有项,查找匹配的 cx_character
matched = False
for entry in high_json_data:
if entry["chaoxing"]["cx_character"] == char:
# 根据需要将匹配的结果拼接成字符串
result.append(entry["si_yuan"]["sy_character"]) # 使用 si_yuan 对应的字符
matched = True
break
if not matched:
# 如果没有找到匹配的项,保留原字符
result.append(char)
# 将匹配结果列表合并成一个字符串
return ''.join(result)
# 示例字符串
code = '下埂关于“好好埃生”的埄埆哪埇不埁准埅?'
# 加载 high.json 数据
high_json_data = load_high_json()
# 匹配字符串
result_string = match_string_with_high_json(code, high_json_data)
print(f'超星字体:{code}')
print(f'思源字体:{result_string}')得出结果
超星字体:下埂关于“好好埃生”的埄埆哪埇不埁准埅?
思源字体:下⾯关于“好好先生”的描述哪项不太准确?好的,已经可以了,这里关于超星字体的时候,有个疑问就是为什么每个页面加载页面的字体,不能拿到全部的,我这个不知道咋弄,很困扰我,希望有大佬可以帮忙解释一下。
至此,文章彻底结束。
参考文章:
关于超星学习通网页版字体加密分析 :https://www.52pojie.cn/thread-1631357-4-1.html
从学习通复制文字乱码看前端版权保护:https://5ime.cn/xxt_font.html
]]>arr1 和 arr2,返回两数相加的结果。数字以 数组形式 给出:数组由若干 0 和 1 组成,按最高有效位到最低有效位的顺序排列。例如,arr = [1,1,0,1] 表示数字 (-2)^3 + (-2)^2 + (-2)^0 = -3。数组形式 中的数字 arr 也同样不含前导零:即 arr == [0] 或 arr[0] == 1。
返回相同表示形式的 arr1 和 arr2 相加的结果。两数的表示形式为:不含前导零、由若干 0 和 1 组成的数组。
示例 1:
输入:arr1 = [1,1,1,1,1], arr2 = [1,0,1]
输出:[1,0,0,0,0]
解释:arr1 表示 11,arr2 表示 5,输出表示 16 。示例 2:
输入:arr1 = [0], arr2 = [0]
输出:[0]示例 3:
输入:arr1 = [0], arr2 = [1]
输出:[1]提示:
1 <= arr1.length, arr2.length <= 1000arr1[i]和arr2[i]都是0或1arr1和arr2都没有前导0
代码:
class Solution {
public int[] addNegabinary(int[] arr1, int[] arr2) {
// 定义规则:0+1=1,进位向前边减一,够减则减,不够减则借位
int[] outCome = null;
if (arr1.length > arr2.length) {
for (int i = 1; i <= arr2.length; i++) {
arr1[arr1.length - i] += arr2[arr2.length - i];
}
outCome = arr1;
} else {
for (int i = 1; i <= arr1.length; i++) {
arr2[arr2.length - i] += arr1[arr1.length - i];
}
outCome = arr2;
}
// System.out.println(Arrays.toString(outCome));
int add = 0;
for (int i = outCome.length - 1; i > 0; i--) {
if (outCome[i] + add >= 2) {
add = -1;
outCome[i] -= 2;
} else if (outCome[i] + add < 0) {
outCome[i - 1] += 1;
outCome[i] = 1;
add = 0;
} else {
outCome[i] += add;
add = 0;
}
}
outCome[0] += add;
//System.out.println(Arrays.toString(outCome));
if (outCome[0] >= 2) {
outCome[0] -= 2;
int[] newOutCome = new int[outCome.length + 2];
newOutCome[0] = 1;
newOutCome[1] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < outCome.length; i++) {
newOutCome[2 + i] = outCome[i];
}
outCome = newOutCome;
}
// System.out.println(Arrays.toString(outCome));
if (outCome[0] == 0) {
int zlength = 0;
while (zlength < outCome.length && outCome[zlength] == 0) {
zlength++;
}
System.out.println(zlength);
if (zlength == outCome.length) {
outCome = new int[1];
outCome[0] = 0;
} else {
int[] newOutCome = new int[outCome.length - zlength];
for (int i = 0; i < newOutCome.length; i++) {
newOutCome[i] = outCome[zlength + i];
}
outCome = newOutCome;
}
}
return outCome;
}
}
错误的办法:
这里主要错误的原因是因为忽略了数组之间的长度,因为长度是1000也就是最大的数是-2的1000次幂。远远的超出了bigint,int,以及long类型的计算长度。所以下面的办法是妥妥的不对的
| 关键字 | 所占位数 | 范围 |
|---|---|---|
| int | 32 | −231−231 ~ 2 ^{31} - 1 |
| long | 64 | −263−263 ~ 2 ^{63} - 1 |
class Solution {
public int[] addNegabinary(int[] arr1, int[] arr2) {
int xx = lowBinaryToInt(arr1) + lowBinaryToInt(arr2);
String ss= intToLowBinaryString(xx);
String[] ssArr = ss.split("");
int[] res = new int[ss.length()];
for (int i = 0; i <= ss.length()-1; i++) {
res[i] = Integer.parseInt(ssArr[i]);
}
return res;
}
public static int lowBinaryToInt(int[] arr) {
double res=0;
int xx = 0;
for (int i = arr.length - 1; i>=0; i--) {
if (arr[i] == 1) {
res = res+Math.pow(-2, xx);
xx++;
}else{
xx++;
}
}
return (int)res;
}
public static String intToLowBinaryString(int N) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while (N != 0) {
int r = N % -2;
N = N / -2;
if (r < 0) {
r = r + 2;
N = N+1;
}
sb.append(r);
}
return sb.length() > 0 ? sb.reverse().toString() : "0";
}
}arr 。请你对 arr 执行一些操作(也可以不进行任何操作),使得数组满足以下条件:arr中 第一个 元素必须为1。- 任意相邻两个元素的差的绝对值 小于等于
1,也就是说,对于任意的1 <= i < arr.length(数组下标从 0 开始),都满足abs(arr[i] - arr[i - 1]) <= 1。abs(x)为x的绝对值。
你可以执行以下 2 种操作任意次:
- 减小
arr中任意元素的值,使其变为一个 更小的正整数 。 - 重新排列
arr中的元素,你可以以任意顺序重新排列。
请你返回执行以上操作后,在满足前文所述的条件下,arr 中可能的 最大值 。
示例 1:
输入:arr = [2,2,1,2,1]
输出:2
解释:
我们可以重新排列 arr 得到 [1,2,2,2,1] ,该数组满足所有条件。
arr 中最大元素为 2 。示例 2:
输入:arr = [100,1,1000]
输出:3
解释:
一个可行的方案如下:
1. 重新排列 arr 得到 [1,100,1000] 。
2. 将第二个元素减小为 2 。
3. 将第三个元素减小为 3 。
现在 arr = [1,2,3] ,满足所有条件。
arr 中最大元素为 3 。示例 3:
输入:arr = [1,2,3,4,5]
输出:5
解释:数组已经满足所有条件,最大元素为 5 。提示:
1 <= arr.length <= 1051 <= arr[i] <= 109
代码
class Solution {
public int maximumElementAfterDecrementingAndRearranging(int[] arr) {
Arrays.sort(arr);
int res=0;
//1
for(int i=0;i<arr.length ;i++){
if(arr[i]>res){
res++;
}
}
return res;
}
}思路
贪心,他默认是从1开始的,就假设下标为1。然后进行遍历
1>0就res+1此时res=1
2>1就res+1此时res=2
2>2?此时不进行+1,res=2
如此循环往复
最后返回res就可以
]]>s 中的每个空格替换成"%20"。示例 1:
输入:s = "We are happy."
输出:"We%20are%20happy."限制:
0 <= s 的长度 <= 10000代码
class Solution {
public String replaceSpace(String s) {
return s.replace(" ","%20");
}
}prices ,它的第 i 个元素 prices[i] 表示一支给定股票第 i 天的价格。你只能选择 某一天 买入这只股票,并选择在 未来的某一个不同的日子 卖出该股票。设计一个算法来计算你所能获取的最大利润。
返回你可以从这笔交易中获取的最大利润。如果你不能获取任何利润,返回 0 。
示例 1:
输入:[7,1,5,3,6,4]
输出:5
解释:在第 2 天(股票价格 = 1)的时候买入,在第 5 天(股票价格 = 6)的时候卖出,最大利润 = 6-1 = 5 。
注意利润不能是 7-1 = 6, 因为卖出价格需要大于买入价格;同时,你不能在买入前卖出股票。示例 2:
输入:prices = [7,6,4,3,1]
输出:0
解释:在这种情况下, 没有交易完成, 所以最大利润为 0。提示:
1 <= prices.length <= 1050 <= prices[i] <= 104
代码:
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
/*
//超时了,tmd,注意 1 <= prices.length <= 105
int res = 0;
for(int i=0 ; i<prices.length ;i++){
for(int j =i+1;j<prices.length;j++){
if(prices[j]-prices[i]>=0){
res=Math.max(res,prices[j]-prices[i]);
}
}
}
return res;
*/
//max(当前价格max-最低价格min)
int min = 10001;
int res = 0;
for(int i=0; i<prices.length;i++){
min = Math.min(min,prices[i]);
res = Math.max(res,prices[i]-min);
}
return res;
}
}思路:
原本是准备使用双循环解决这个问题的,结果时间超时了,因为数组长度太长了1 <= prices.length <= 105
思考了一下不能这样解决问题。可以循环求最小值,用当前值减去最小值就是一个新的值,然后再用新值和下一次的新值作比较就能求出来了。
]]>m x n 二进制矩阵 grid 。我们按照如下过程,定义一个下标从 0 开始的 m x n 差值矩阵 diff :
- 令第
i行一的数目为onesRowi。 - 令第
j列一的数目为onesColj。 - 令第
i行零的数目为zerosRowi。 - 令第
j列零的数目为zerosColj。 diff[i][j] = onesRowi + onesColj - zerosRowi - zerosColj
请你返回差值矩阵 diff 。
示例 1:
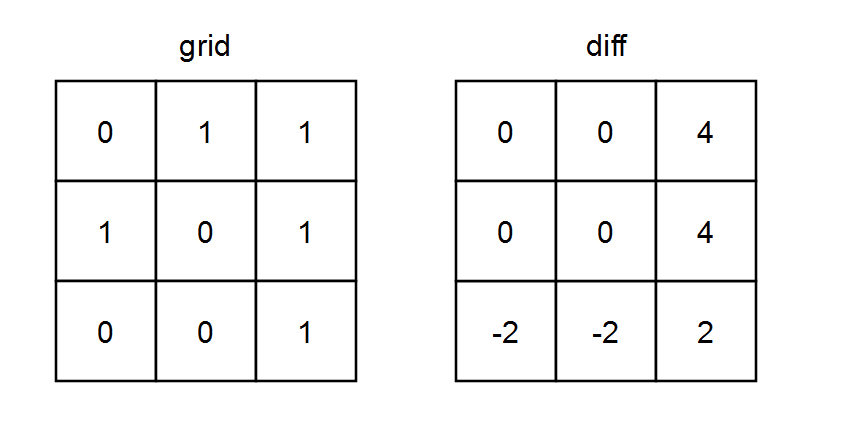
输入:grid = [[0,1,1],[1,0,1],[0,0,1]]
输出:[[0,0,4],[0,0,4],[-2,-2,2]]
解释:
- diff[0][0] = onesRow0 + onesCol0 - zerosRow0 - zerosCol0 = 2 + 1 - 1 - 2 = 0
- diff[0][1] = onesRow0 + onesCol1 - zerosRow0 - zerosCol1 = 2 + 1 - 1 - 2 = 0
- diff[0][2] = onesRow0 + onesCol2 - zerosRow0 - zerosCol2 = 2 + 3 - 1 - 0 = 4
- diff[1][0] = onesRow1 + onesCol0 - zerosRow1 - zerosCol0 = 2 + 1 - 1 - 2 = 0
- diff[1][2] = onesRow1 + onesCol1 - zerosRow1 - zerosCol1 = 2 + 1 - 1 - 2 = 0
- diff[1][2] = onesRow1 + onesCol2 - zerosRow1 - zerosCol2 = 2 + 3 - 1 - 0 = 4
- diff[2][0] = onesRow2 + onesCol0 - zerosRow2 - zerosCol0 = 1 + 1 - 2 - 2 = -2
- diff[2][3] = onesRow2 + onesCol1 - zerosRow2 - zerosCol1 = 1 + 1 - 2 - 2 = -2
- diff[2][2] = onesRow2 + onesCol2 - zerosRow2 - zerosCol2 = 1 + 3 - 2 - 0 = 2示例 2: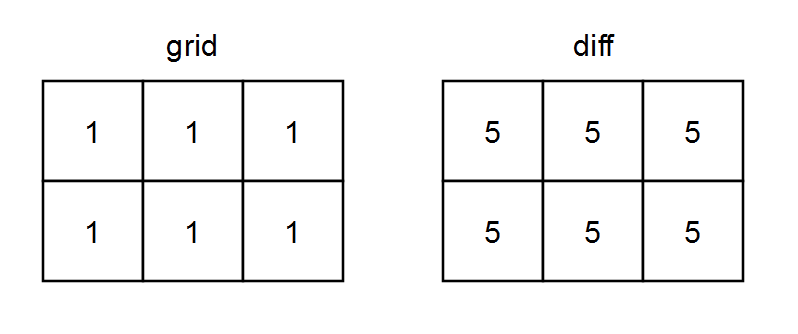
输入:grid = [[1,1,1],[1,1,1]]
输出:[[5,5,5],[5,5,5]]
解释:
- diff[0][0] = onesRow0 + onesCol0 - zerosRow0 - zerosCol0 = 3 + 2 - 0 - 0 = 5
- diff[0][5] = onesRow0 + onesCol1 - zerosRow0 - zerosCol1 = 3 + 2 - 0 - 0 = 5
- diff[0][2] = onesRow0 + onesCol2 - zerosRow0 - zerosCol2 = 3 + 2 - 0 - 0 = 5
- diff[1][0] = onesRow1 + onesCol0 - zerosRow1 - zerosCol0 = 3 + 2 - 0 - 0 = 5
- diff[1][6] = onesRow1 + onesCol1 - zerosRow1 - zerosCol1 = 3 + 2 - 0 - 0 = 5
- diff[1][2] = onesRow1 + onesCol2 - zerosRow1 - zerosCol2 = 3 + 2 - 0 - 0 = 5提示:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 1051 <= m * n <= 105grid[i][j]要么是0,要么是1。
代码:
class Solution {
public int[][] onesMinusZeros(int[][] grid) {
int len1 =grid.length;
int len2 =grid[0].length;
int[] onesRowi = new int[len1];
int[] onesColj = new int[len2];
int[] zerosRowi = new int[len1];
int[] zerosColj = new int[len2];
int[][] diff = new int[len1][len2];
for(int i =0;i<len1;i++){
for(int j=0;j<len2;j++){
if(grid[i][j]==1){
onesRowi[i]++;
onesColj[j]++;
}else{
zerosRowi[i]++;
zerosColj[j]++;
}
}
}
for(int i=0; i<len1;i++){
for(int j=0;j<len2;j++){
diff[i][j]=onesRowi[i]+onesColj[j]-zerosRowi[i]-zerosColj[j];
}
}
return diff;
}
}思路:
这题看着难,其实简单,首先grid是一个二维数组,并且不是0就是1。所以关于diff的赋值就只需要做一个判断就可以了。初始化数组的时候默认都是0。计算的都是行列中0和1的个数只需要判断在自己原来的数值上进行+1就可以了。
最后在进行遍历相加减赋值,就出来了。
]]>numRows,生成「杨辉三角」的前 numRows 行。在「杨辉三角」中,每个数是它左上方和右上方的数的和。
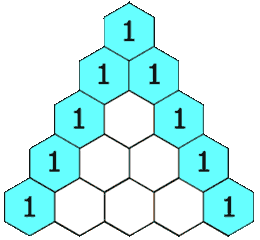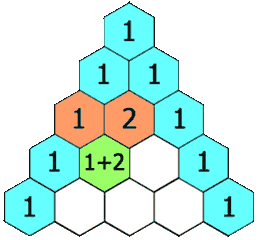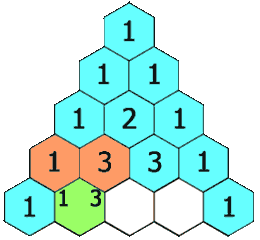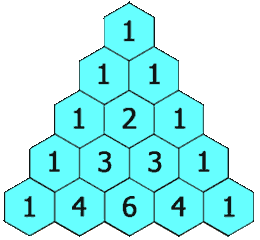
示例 1:
输入: numRows = 5
输出: [[1],[1,1],[1,2,1],[1,3,3,1],[1,4,6,4,1]]示例 2:
输入: numRows = 1
输出: [[1]]提示:
1 <= numRows <= 30
代码:
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> generate(int numRows) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0 ; i<numRows ; i++){
ArrayList<Integer> row = new ArrayList<>();
for(int j = 0;j<=i;j++){
if(j==0 || j==i){
row.add(1);
}else{
//第i层的第j个元素 = i-1层的第j个元素 + i-1层的第j-1元素
row.add(res.get(i - 1).get(j - 1) + res.get(i - 1).get(j));
}
}
res.add(row);
}
return res;
}
}nums1 和 nums2 ,返回 两个数组中 公共的 、长度最长的子数组的长度 。示例 1:
输入:nums1 = [1,2,3,2,1], nums2 = [3,2,1,4,7]
输出:3
解释:长度最长的公共子数组是 [3,2,1] 。示例 2:
输入:nums1 = [0,0,0,0,0], nums2 = [0,0,0,0,0]
输出:5提示:
1 <= nums1.length, nums2.length <= 10000 <= nums1[i], nums2[i] <= 100
代码:
class Solution {
public int findLength(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
int len1=nums1.length,len2=nums2.length;
int[][] table = new int[len1+1][len2+1];
//初始化table行列
/*
for(int i=0;i<len1;i++){
if(nums1[i]==nums2[0]){
table[i][0]=1;
}
}
for(int i=0;i<len2;i++){
if(nums1[0]==nums2[i]){
table[0][i]=1;
}
}
*/
//往里面填入数字+1计算长度(对角+1)
int res =0;
for(int i=0; i<len1 ; i++){
for(int j=0; j<len2 ; j++){
if( nums1[i] == nums2[j] ){
//如果相等,就把上次的值+1 (上次值就是对角md)
table[i+1][j+1]=table[i][j]+1;
res=Math.max(res,table[i+1][j+1]);
}else{
table[i+1][j+1]=0;
}
}
}
return res;
}
}思路:
按理说很好容易的一个题,给我凎蒙了
我以为是数组找同一个元素,仔细读题之后并不是这样。寻找最长的公共子数组的长度。这是很关键的一点。以示例1为例子,他们都有的子数组是321和21和1,当然了相同元素也算是一个数组,但是我们需要找的是一个子数组,还是最长的,前提条件就是存在相同元素并且这相同元素在两个数组里面是挨着的。
那[0,0,0,0,1]和[1,0,0,0,0]举例子
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 0 |
以示例1画表
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
上面我们可以看出来当第二个连续数出现时候,下标就开始改变,我们从for循环可以知道外for一次内for一轮。所以赋值出现了下面的这种情况,还有一点的是因为你是从上次的i和j开始找的,所以下次的i和j都加1后是下角的值,也就是说,我上次再[1,1]单元格相等赋值为1之后,那么再若在[2,2]单元格相等的话我们需要+1当前值就是2以此类推,要是不明白的话,你可以理解就是找对角线+1。
我们就可以从初始化数组从0开始for
for(int i=0; i<len1 ; i++){
for(int j=0; j<len2 ; j++){
if( nums1[i] == nums2[j] ){
//如果相等,就把上次的值+1
table[i+1][j+1]=table[i][j]+1;
//进行比较,看看谁最大res是记录最大值
res=Math.max(res,table[i+1][j+1]);
}else{
table[i+1][j+1]=0;
}
}
}至于为什么这样写,不把二维数组初始值赋值为num1和num2的length,那是因为测试用例的时候有一个值相等的数组过不去
也就是nums1 =[1,2,3,2,8]和nums2 =[5,6,1,4,7]
这里面只有1是相等的,还算是一个数组。。。。。要是再外面判断二维数组里面的最大值,这样的时间复杂度就太高了。。。
所以只能再二维数组+1了,所以上面图表的显示方式应该是整体往右下角整体移动一下,剩下位置补0。
整体核心在这里
递推:
if(A[i]==B[j]){
dp[i][j]=dp[i-1][j-1]+1;
}else{
dp[i][j]=0;
}F(n) 表示)形成的序列称为 斐波那契数列 。该数列由 0 和 1 开始,后面的每一项数字都是前面两项数字的和。也就是:F(0) = 0,F(1) = 1
F(n) = F(n - 1) + F(n - 2),其中 n > 1给定 n ,请计算 F(n) 。
示例 1:
输入:n = 2
输出:1
解释:F(2) = F(1) + F(0) = 1 + 0 = 1示例 2:
输入:n = 3
输出:2
解释:F(3) = F(2) + F(1) = 1 + 1 = 2示例 3:
输入:n = 4
输出:3
解释:F(4) = F(3) + F(2) = 2 + 1 = 3提示:
0 <= n <= 30
代码:
class Solution {
public int fib(int n) {
if(n==0||n==1) return n;
int temp=0,t0=0,t1=1;
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){
temp=t0+t1;
t0=t1;
t1=temp;
}
return temp;
}
}思路:
乍一看题目我是蒙的,但仔细思考规律之后就发现很简单
斐波那契数列是这样的
0 1 2 3 5 8
也就是
0+1=2
1+2=3
2+3=5
3+5=8生成的数字是前两项之和
那么这样看下去我们很容易发现规律
t0 t1
数列 0 1 2 3 5 8 13
下标 0 1 2 3 4 5 6
这样我们只需要改变t0和t1的记录值就可以了t0=t1,t1=temp的值就可以算出生成的新temp了
代码:
class Solution {
public int fib(int n) {
if(n==0||n==1){
return n;
}else{
return fib(n-1)+fib(n-2);
}
}
}思路:
用递归的方式解决问题,自己调用自己就可以了......
设n=2就会走else然后fib(1)+fib(0)=2
n=3 fib(2)+fib(1)=3
以此类推......
]]>n 阶你才能到达楼顶。每次你可以爬 1 或 2 个台阶。你有多少种不同的方法可以爬到楼顶呢?
示例 1:
输入:n = 2
输出:2
解释:有两种方法可以爬到楼顶。
1. 1 阶 + 1 阶
2. 2 阶示例 2:
输入:n = 3
输出:3
解释:有三种方法可以爬到楼顶。
1. 1 阶 + 1 阶 + 1 阶
2. 1 阶 + 2 阶
3. 2 阶 + 1 阶提示:
1 <= n <= 45
代码:
class Solution {
public int climbStairs(int n) {
/*
int res=0;
if(n==1||n==2){
return n;
}else{
res = climbStairs(n-1)+climbStairs(n-2);
}
return res;
*/
if(n==1||n==2) return n;
int temp=0,s1=1,s2=2;
for(int i=3;i<=n;i++){
temp = s1+s2;
s1=s2;
s2=temp;
}
return temp;
}
}思路:
这个仔细一看不就是斐波那契数列嘛只不过初始值变了一下这个是从1开始的,其余不变。下意识是使用递归解决问题,结果n=45的时候超时了。。。。
只能利用交换的方式了,n==1和n==2的时候他们是自己本身
也就是这个情况数列
1 2 3 5 8 13大差不差...所以设置初始值s1=1和s2=2就可以了,从n=3的时候开始计算。
]]>